28/03/2025 / Health and Fitness
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Heart Health
Learn the relationship between Omega 3 fatty acids and heart health. Discover how Omega 3 fatty acids can help prevent cardiovascular diseases, their recommended dosage, sources etc.

Table of Content
Introduction
While the headlines about heart disease prevention come and go, Omega 3 fatty acids have maintained their position for a long time. Omega 3 fatty acids are versatile in their mechanism of action to protect the heart. Several research studies, like the REDUCE-IT trial and the VITAL study, showed the beneficial effects of Omega 3 fatty acid in reducing cardiovascular mortality in high-risk patients.
Omega 3 fatty acids can lower triglyceride levels and lower blood pressure, as well as they can reduce the inflammation in blood vessels. In this blog, We'll cover What are Omega 3 fatty acids, What is the relationship between Omega 3 fatty acids and heart health, Sources of Omega 3 fatty acids, etc.
What are Omega 3 Fatty acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids which are important for cardiovascular health. Our body cannot produce Omega-3 Fatty acids by itself; therefore, We need to obtain them from our diet. The relationship between Omega 3 fatty acids and heart health has been established through various clinical studies, which include the VITAL study and REDUCE-IT study; the studies have shown a decreased risk of heart attack and overall improvement in cardiovascular health.
There can be different types of Omega 3 fatty acids:
EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid): EPA is found in fatty fish and is known to reduce inflammation in the blood vessels and improve cardiovascular health.
DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid): DHA has not only a role in cardiovascular health, but it also has a role in stabilizing the neurons in our brain.
ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid): ALA is a type of Omega 3 fatty acid which is derived from plant sources; it can be converted into EPA and DHA, although this conversion is not that effective.
Relation between Omega 3 Fatty acids and Heart Health
Data from several studies have shown that supplementation of Omega 3 fatty acid supplementation in high-risk individuals or people with heart disease has reduced overall Cardiovascular Mortality. Similar Results are given by the American Heart Association that supplementary Omega 3 fatty acids in a population with low fish intake have improved outcomes in people with cardiovascular diseases.

What is the relationship between Omega 3 fatty acids and heart health:
Reduce inflammation: Inflammation plays a key role in the development of cardiovascular diseases omega-3 fatty acids can reduce inflammatory markers like CRP, IL-6, and TNF-alpha. Reduced Inflammation in blood vessels contributes to the beneficial effects of Omega-3 Fatty acids.
Improve cholesterol levels: Omega-3 fatty acids increase HDL levels and lower triglyceride levels due to these properties Omega-3 Fatty acids can prevent plaque formation in the blood vessels. Plaque formation is a risk factor and can contribute to the development of Heart attack or stroke.
Stabilize heart rhythm: Studies have shown that Omega 3 fatty acid can stabilize heart rhythm by reducing arrhythmia, which can further prevent sudden cardiac death. Treatment of arrhythmias includes drugs. Omega-3 fatty acids are not used in the treatment of arrhythmias.
Lower blood pressure: studies have shown that Omega 3 fatty acids can reduce both systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Thus, they lower blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Prevent blood clot formation: Omega 3 fatty acids reduce platelet aggregation. Platelet aggregation is an important step in clot formation. Therefore, it reduces the risk of the development of stroke and heart attack.
Scientific evidence of Omega 3 Fatty acids and Heart health:
REDUCE-IT trial: This study has shown that giving icosapent ethyl (a type of omega-3 fatty acid) to patients with high triglyceride levels has reduced the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases. This study has shown a substantial 25% decrease in risk reduction compared to the group.
Other studies have also been done, including the VITAL Study and STRENGTH trial, but the results were not that significant. They used a combination of Omega-3 fatty acids or Combined with Vitamin D.
Natural sources of Heart healthy Omega-3 fatty acids
It is always better to obtain Omega-3 fatty acids from dietary sources rather than to take supplements. Before taking supplements it is always advisable to consult your Doctor. Here are some Natural sources of heart-healthy Omega 3 fatty acids:
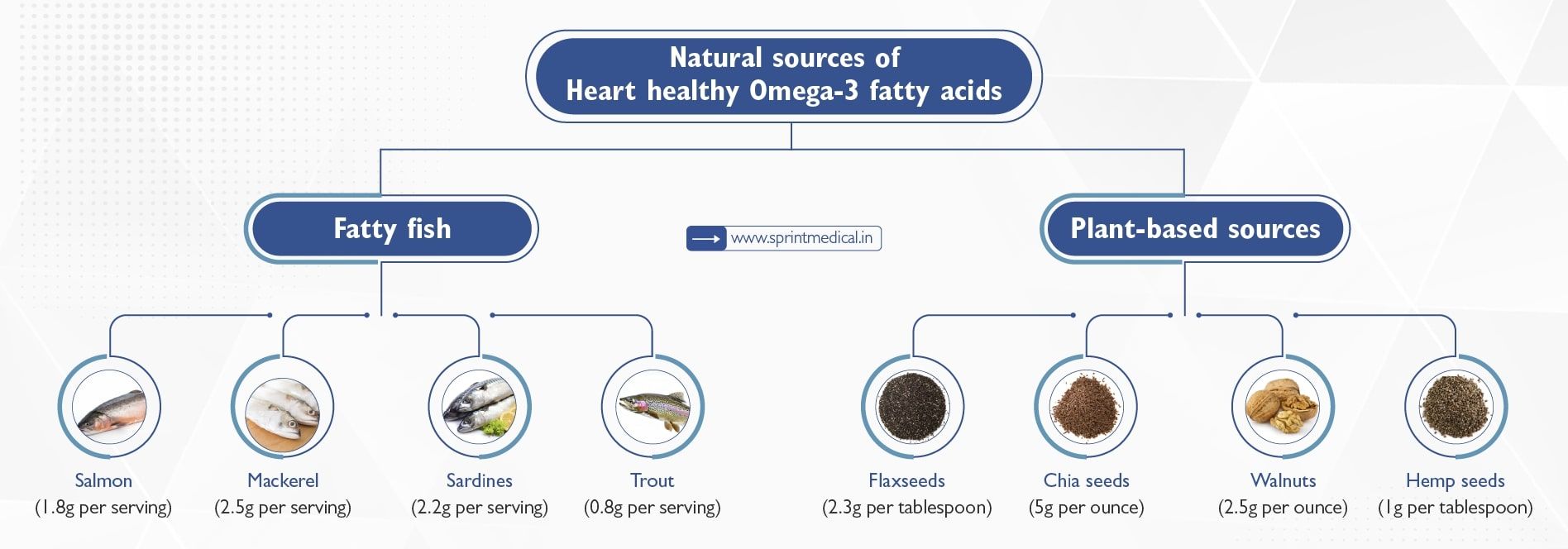
Fatty fish: Fatty fish is high in EPA and DHA. You consume
Salmon (1.8g per serving)
Mackerel (2.5g per serving)
Sardines (2.2g per serving)
Trout (0.8g per serving).
Plant-based sources of Omega-3 fatty acids:
Flaxseeds (2.3g per tablespoon)
Chia seeds (5g per ounce)
Walnuts (2.5g per ounce)
Hemp seeds (1g per tablespoon)
Plant-based sources are rich in ALA, not in EPA and DHA. ALA is poorly converted into EPA and DHA. EPA and DHA are directly utilised by our body; It is recommended to consume fish for Omega-3 fatty acids rather than Plant sources.
Omega 3 fatty acids enriched foods include Algae-based supplements and fortified eggs.
Dietary intake vs Supplements: Consumption of Omega-3 Fatty acids is always recommended through dietary sources as A Balanced diet can provide other minerals and antioxidants, which can reduce the risk of Cardiovascular disease. Supplements can be helpful for those who cannot consume adequate amounts of Omega-3 fatty acids from their diet.
How much Omega-3 do you need? The American Heart Association recommends 1 to 2 servings of fatty fish per week to get the recommended amount of Omega 3 fatty acids and Heart health benefits.
Adding Omega-3 Fatty Acids to Your Diet
Getting Omega 3 fatty acids from your diet is more beneficial than taking supplements here are some tips to include Omega 3 fatty acids in your diet:
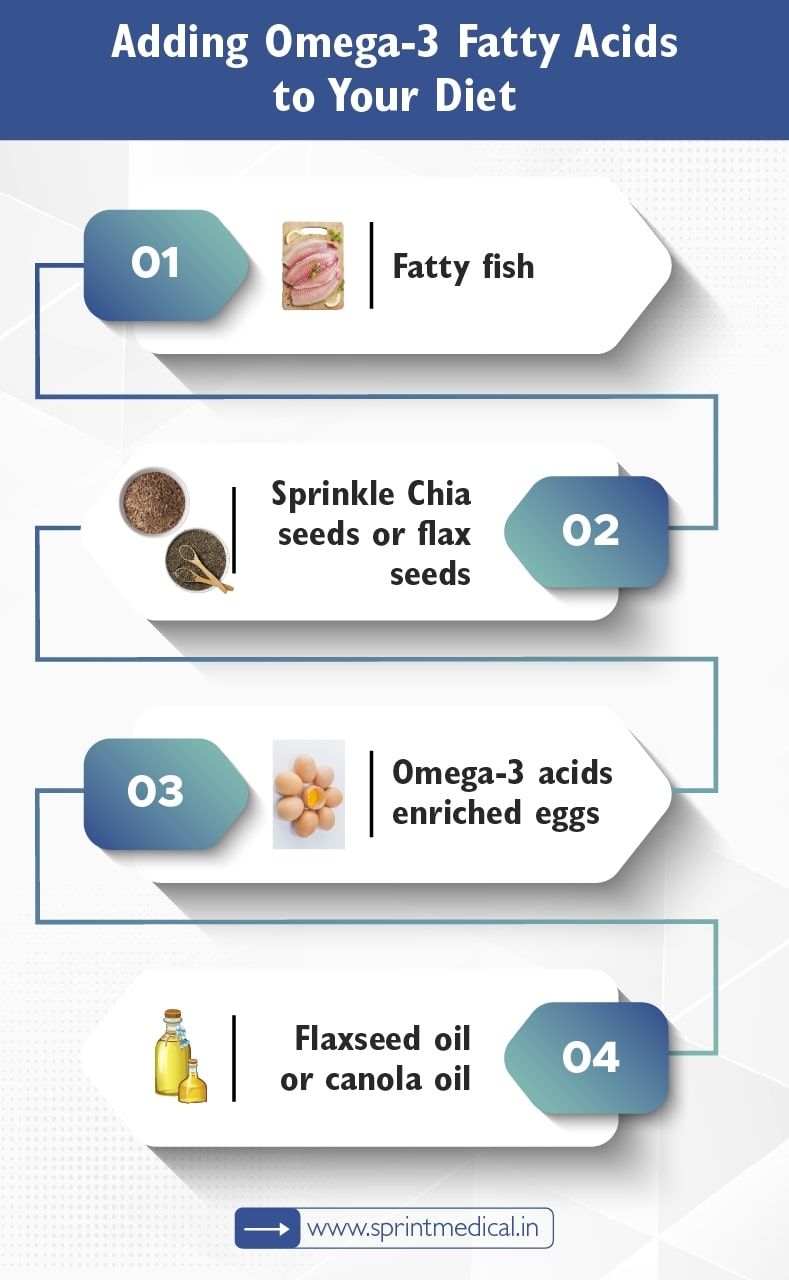
Fatty fish: Include fatty fish 2 servings per week
Sprinkle Chia seeds or flax seeds: You can sprinkle Chia seeds or flax seeds to your salads oatmeals and yoghurt
Omega-3 acids enriched eggs: you can opt for Omega 3 acid enriched eggs and then choose normal eggs
Flaxseed oil or canola oil: You can use flaxseed oil or canola oil for cooking purposes.
Tips for consuming supplements:
Take Omega 3 acid supplement with food because it gets absorbed easily with fats.
Store in a cool and dark place.
Opt for quality brands
It is important to keep in mind that only consuming Omega 3 fatty acids for the heart does not help. You need to include heart-healthy lifestyle modifications to keep your heart healthy.
Exercise: Exercise regularly 30 minutes per day, 5 days a week, or 150 minutes per week of moderate activity.
Reduce consumption of Ultra-processed food and trans fat
Manage stress through meditation
Consume a fibre-rich diet: Consuming a high-fibre diet has shown beneficial effects on cholesterol levels as well as other cardiovascular diseases.
Omega-3 Fatty acids supplements and Considerations
People who struggle to get enough Omega 3 fatty acid from their diet can opt for an Omega 3 fatty acid supplement. Here are some available varieties:
Fish oil supplement: Commonly contains EPA and DHA.
Algae Oil supplement: these can be suited for vegetarians and Vegans
Krill oil supplement: More bioavailability but expensive.
Cod liver supplement: These contain vitamins A and D in addition to Omega 3 fatty acids.
Risks and considerations:
Mercury contamination: Omega 3 fatty acids can be contaminated with Mercury; therefore, choose Omega 3 fatty acids with third-party testing.
Oxidation risk: Omega 3 fatty acid supplements can get oxidised and spoiled easily; therefore, choose supplements which have antioxidants like vitamin E.
Drug interactions: A high dose of Omega 3 fatty acids can interact with blood thinners like warfarin and can increase the bleeding risk.
Some people can face digestive issues.
Take-Home Points
Omega 3 fatty acids are versatile in their mechanism of action to protect the heart.
Omega 3 fatty acids can lower triglyceride levels and lower blood pressure, as well as they can reduce the inflammation in blood vessels.
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids which are important for cardiovascular health.
There are three types of Omega 3 fatty acids EPA, DHA and ALA
Data from several studies have shown that supplementation of Omega 3 fatty acid supplementation in high-risk individuals or people with heart disease has reduced overall Cardiovascular Mortality.
Natural sources of Omega 3 fatty acids include Fatty fish, chia seeds, flaxseeds, walnuts, hemp seeds etc.
Consumption of Omega-3 Fatty acids is always recommended through dietary sources
Supplements can be helpful for those who cannot consume adequate amounts of Omega-3 fatty acids from their diet.
The American Heart Association recommends 1 to 2 servings of fatty fish per week to get the recommended amount of Omega 3 fatty acids and Heart health benefits.
References
FAQ on Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Heart Health
The American Heart Association recommends 1 to 2 servings of fatty fish per week to get the recommended amount of Omega 3 fatty acids and Heart health benefits.
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids which are important for cardiovascular health.
You can consume Natural sources of Omega 3 fatty acids, which include Fatty fish, chia seeds, flaxseeds, walnuts, hemp seeds, etc. You can take supplements if you're not able to meet your requirements through diet.
Yes, Omega 3 fatty acids help heart health by lowering the triglyceride level and lowering blood pressure, as well as reducing the inflammation in blood vessels.
People who are on blood thinners, affected by chronic diseases like diabetes and cardiovascular Diseases. Always consult your doctor before starting Supplements.
Some major side effects of Omega 3 fatty acids include Allergic reactions like rash; hives; itching; red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin with or without fever; wheezing; tightness in the chest or throat; trouble breathing etc.
Comments ( 0 )
No Comments
Leave a Comment
Related Posts
Omega 3 fatty acids benefits
An overview of the health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids
Dr. Mrinalinee Roy
How Omega-3 Fatty Acids Affects your Brain Health
Discover the benefits of Omega-3 fatty acids for brain health. Learn how these essential nutrients can improve cognitive function, memory, and overall brain health.
Dr. Jilas Paingeeri
20 Foods that are Rich in Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Discover 20 Foods that are Rich in Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are essential to the body for maintaining a good cardiovascular, pulmonary, endocrine and immune system.
Keerthana A P
Health & Wellness Tips
Subscribe to our blog