31/03/2023 / Digestive Disease & Gastroenterology
Gallstones (Cholelithiasis): Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Gallstones are asymptomatic but lead to complications like gallbladder cancer, pancreatitis. Gallbladder stones treatment includes medications, diet, and laparoscopic surgery.

Table of Content
What are Gallstones or Gallbladder Pathri?
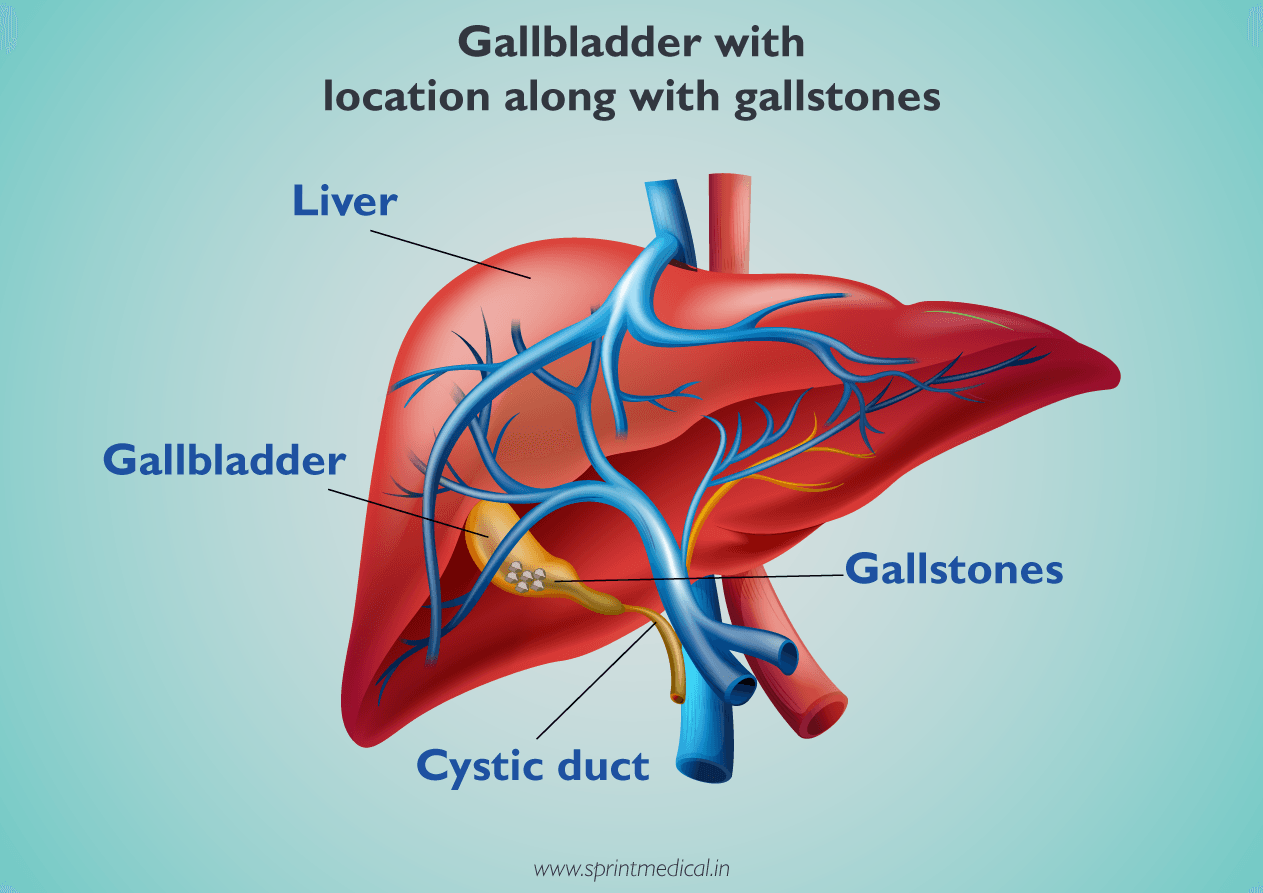
Gallstones or gallbladder pathri are formed within your gallbladder due to the precipitation of bile components. Bile ducts carry bile outside of the liver from the gallbladder. Gallstones are hard, pebble-like particles that are made of cholesterol or bilirubin. Other names of gallstones are cholesterol gallstones and choledocholithiasis.
Most gallstones do not cause any pain or gallstone symptoms known as silent gallstones and they do not require any gallbladder stones treatment. But if left untreated gallstones can cause complications. The size of gallstones can range from grain to the size of a golf ball.
When the gallstone is blocked in the common bile ducts or cystic duct of the biliary tract, this causes abdominal pain in the right upper part resulting in an intense visceral pain called biliary colic or gallbladder attack.
What are the different types of Gallstones?
There are three different types of gallstones, like
Cholesterol stones
Pigment gallstones
Mixed gallstones
1. Cholesterol stones
Cholesterol stones are made up of fats or fatty substances present in the blood usually in a yellow-green color. Cholesterol gallstones are found throughout the body. Cholesterol stones are the most common type of gallstones.
Cholesterol stones can be light yellow to dark green or brown or chalk white in color. The size of cholesterol gallstones is between 2 to 3 cm long with an oval, a tiny and dark central spot.
2. Pigment gallstones
Pigment gallstones are mainly made up of bilirubin, a substance produced when RBC breaks down in the liver. Pigment gallstones appear dark in color. Most people have both cholesterol stones and pigment gallstones. The presence of bilirubin in the blood, skin, and eyes will turn them yellow (leading to jaundice).
Pigment gallstones are commonly seen in people with liver disease, infected bile ducts, and blood disorders like sickle-cell anemia.
3. Mixed gallstones
Mixed gallstones typically contain 20-80% cholesterol, calcium carbonate, palmitate phosphate, bilirubin, and other bile pigments (calcium bilirubinate, calcium palmitate, and calcium stearate)
Signs and symptoms of Gallstones
Gallstones are mostly asymptomatic and do not require any gallbladder stones treatment. Symptomatic gallstones cause pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. This is also accompanied by the presence of nausea and vomiting.
Fever and mild to severe pain between shoulder blades or below the right shoulder for approximately 30 minutes to several hours are effective gallstone symptoms. The other gallbladder symptoms are:
1. Abdominal pain
The occurrence of abdominal pain is one of the gallstone symptoms that will last for 1 to 5 hours in severe cases where the gallbladder contracts. In mild cases, it will last for a few minutes only.
2. Location of pain
The pain occurs in the middle of your abdomen referred to as a tummy. Also, under the ribs on the right-hand side and spreads to the shoulder blades.
The abdominal pain due to the formation of gallstones is called biliary colic. People with gallstones experience excess sweat and feel sick or nauseous or vomit.
Other occasional gallstone symptoms include
Gallstones can cause serious illness if they block the flow of bile in the common bile ducts and cystic ducts into other parts like the pancreas for longer time periods.
At this time, you may experience any or many of the following gallstone symptoms-
Increased body temperature
Skin itching
Yellow color of skin, eyes (jaundice)
Diarrhoea
Dilemma
Loss of appetite
Increased heartbeat
Persistent gallstone symptoms like back pain
Chest pain
These gallbladder symptoms will lead to a gallbladder infection, and liver or pancreas disorders. The gallbladder symptoms may mimic the symptoms of other disorders like pancreatitis or appendicitis. So, if you observe any of these gallbladder symptoms consult a doctor immediately.
What is a Gallbladder attack?
A gallbladder attack is one of the most common gallstone symptoms that causes pain in the upper right abdomen under the rib cage.
A gallbladder attack is observed mostly after the consumption of fatty meals more often at night and after drinking alcohol. Gallbladder stones treatment with medication is sufficient for the reduction of gallbladder attack symptoms.
Other gallbladder attack symptoms are-
Nausea and vomiting
Pain in the right shoulder
Fever
Jaundice
Discoloration of urine
Cause of Gallstones
The cause of gallstones symptoms are still unclear but are caused by the chemical imbalance in the bile fluids of the gallbladder. Gallstones are formed inside the gallbladder due to increased cholesterol and bilirubin.
The chemical imbalances lead to tiny crystals in the bile and they gradually grow into solid stones. Cause of gallstones include factors like obesity and certain dieting. But the research does not fully understand the cause of gallstones.
Complications
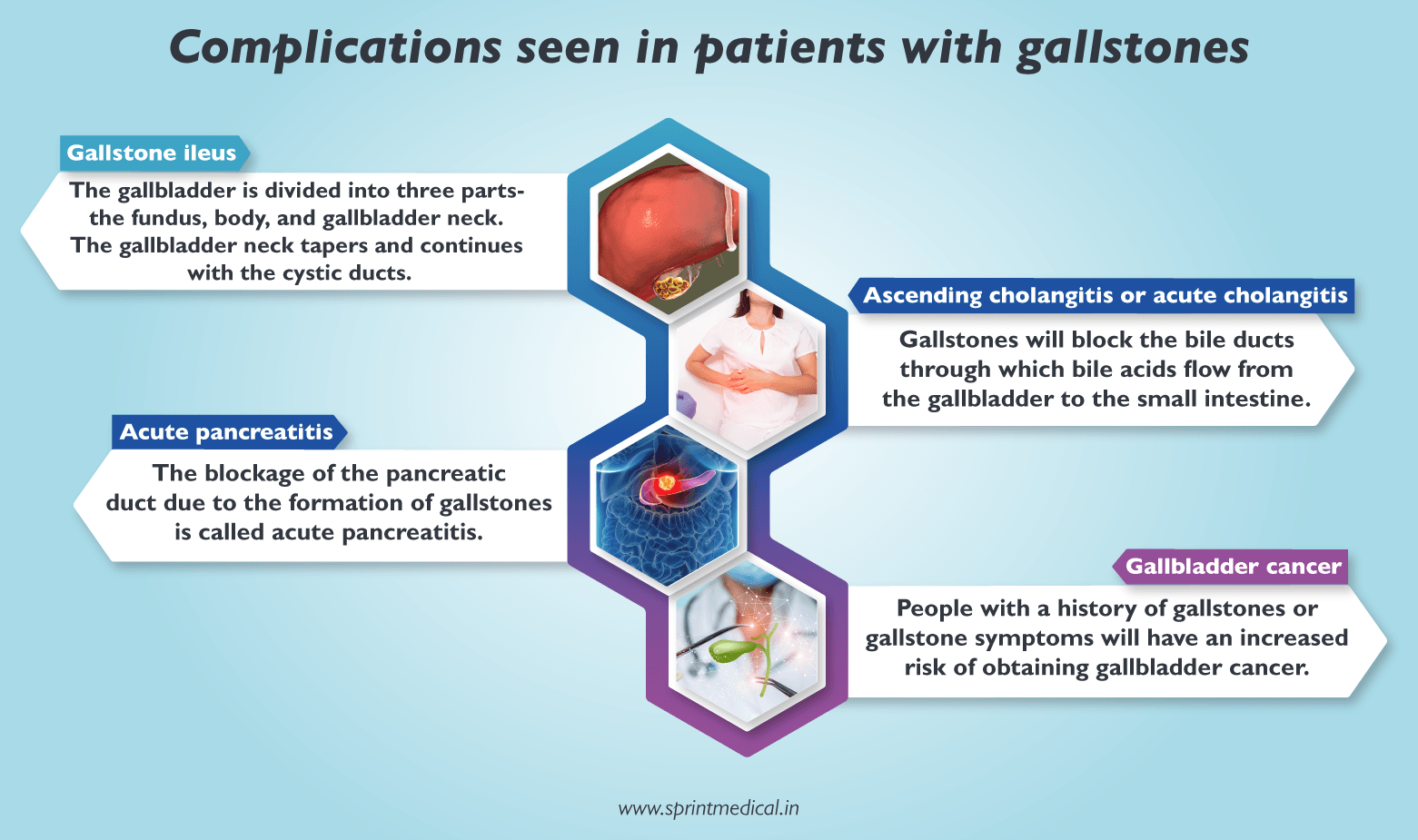
Along with gallstone symptoms, there are other complications seen in patients with gallstones. They are:
Gallstone ileus: The gallbladder is divided into three parts- the fundus, body, and gallbladder neck. The gallbladder neck tapers and continues with the cystic ducts. The formation of gallstones in the gallbladder neck will cause inflammation of the gallbladder called cholecystitis. This will cause severe pain and can lead to fever.
Ascending cholangitis or acute cholangitis: Gallstones will block the bile ducts through which bile acids flow from the gallbladder to the small intestine. This will lead to severe pain, jaundice, and bile ducts infection which can be life-threatening.
Acute pancreatitis: The blockage of the pancreatic duct due to the formation of gallstones is called acute pancreatitis. The pancreatic duct is a long tube that connects the common bile ducts to the pancreas. The pancreatic duct passes pancreatic juices that aid in digestion.
This will cause inflammation of the pancreas, intense and constant abdominal pain that leads to hospitalization.
Gallbladder cancer: People with a history of gallstones or gallstone symptoms will have an increased risk of obtaining gall bladder cancer. Gallbladder cancer occurs in very rare conditions and the elevation of gallbladder cancer will have less risk.
Gallbladder cancer is a disorder of malignant cells that form tissues in your gallbladder. Gallbladder cancer can be treated only in early diagnosis. Symptoms of gallbladder cancer include- abdominal pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, lumps on the abdomen, and jaundice.
Gallbladder cancer can be treated using radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy. Gallbladder cancer therapy treatment can cause side effects.
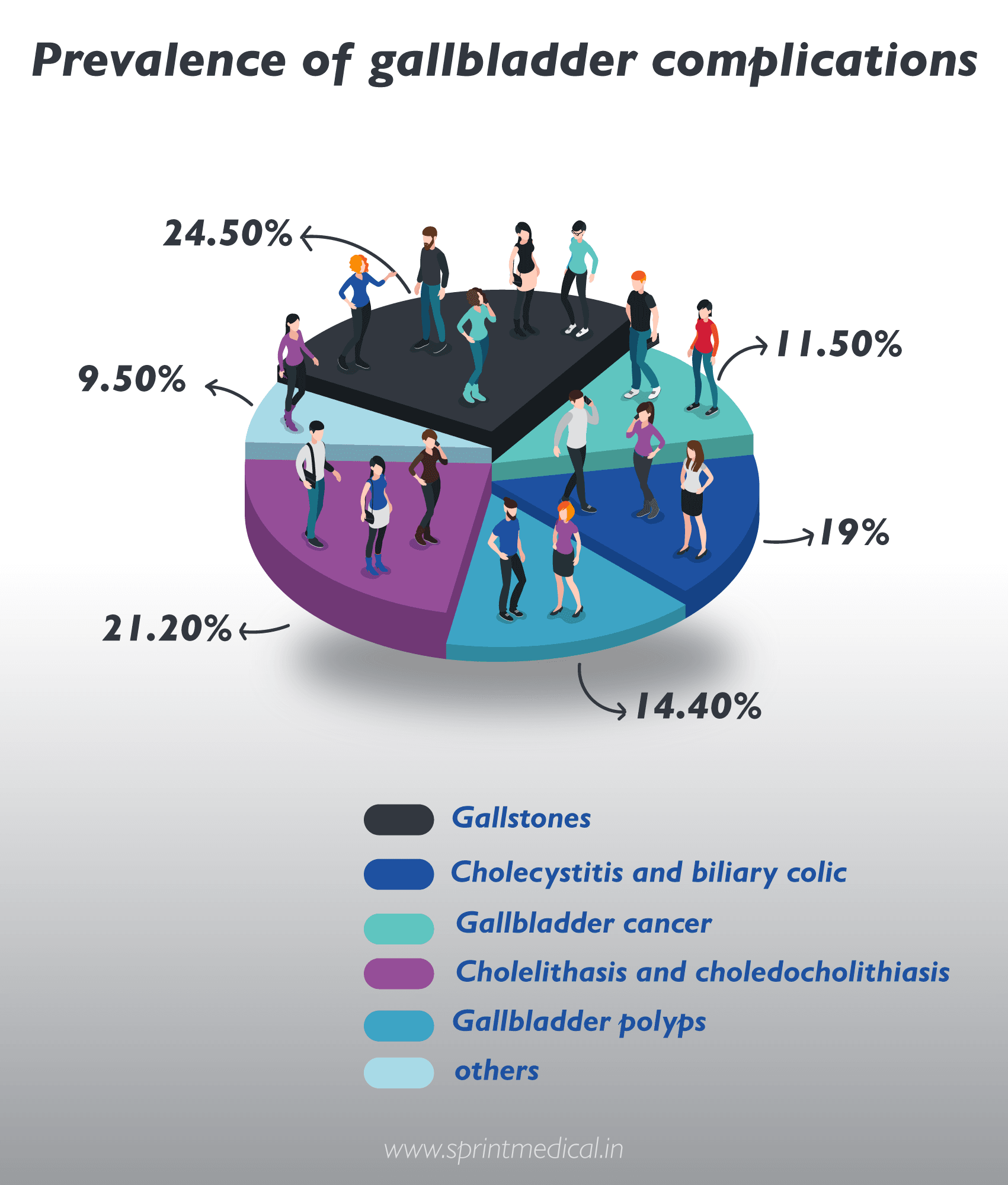
Prevalence of gallbladder complications
Risk factors of Gallstones

Factors that can lead to the risk of gallstones include:
Being female and at an age before menopause near or above 40 years can increase the risk of gallstones and gallbladder cancer
Lack of melatonin can increase the risk of gallstones
North and South Americans and people of Europe have more history of gallstones
The presence of Gilbert syndrome has been found to be associated with an increased risk of gallstones
Combination of factors like body chemistry, body weight gall bladder motility, and a lower-calorie gallstones diet can cause the formation of gallstones
Nutritional factors that will increase the risk of gallstones or constipation, eating few meals per day, low consumption of nutrients like folate, magnesium, calcium, and vitamins, and low fluid consumption.
Men who take a high carbohydrate, glycemic load, and glycemic index diet are at higher risk of gallstones.
Even the rapid decrease of weight will increase the risk of gallstones
The use of Orlistat a drug that decreases body weight will have an increased risk of gallstones and gallbladder cancer.
Deficiency of cholecystokinin during celiac disease also increases the risk of gallstone formation.
Haemolytic anemia, cirrhosis, and biliary tract infections are major risk factors for pigment gallstones formation.
Patients with erythropoietic protoporphyria have an increased risk of gallstones.
Long term use of proton pump inhibitor will decrease gallbladder function leading to the formation of gallstones.
Use of medications that will alter the cholesterol synthesis and concentration in the common bile ducts or cystic ducts is associated with the risk of gallstones.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of many patients with gallstone symptoms does not include a special medical examination with a professional. The diagnosis and detection of gallbladder cancer are difficult. In most cases, gallstone symptoms are discovered when testing for other diseases in people with gallstones. The confirmation for people with gallstones is done through a cholesterol test, an ultrasound scan, a blood test, or an X-ray.
1. Blood test
A blood test for gallstones diagnosis involves testing for the presence of infection, blockage, pancreatitis, or jaundice.
2. Cholangiography
Using the endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) technique a needle is injected into the bloodstream of the cystic duct or bile ducts or common bile ducts. The dye in the ERCP test is visible on the x-ray history of gallstones.
The doctor will see for the presence of dye in any of the ducts and confirms corresponding gallbladder or bile ducts disorders such as the pancreas. The dye does not move to the mentioned body part if there is a formation of gallstones that block the passage for dye.
An expert in the field can locate the area of gallstones, or you can use dye to locate the gallstones area in x-rays.
3. CT scan
This is a non-invasive (without incision) x-ray test that provides cross-sectional pictures of people with gallstones.
4. Cholescintigraphy (HIDA scan)
A small amount of radioactive material is injected into the gallbladder for gallstones diagnosis. After the injection, the gallbladder contracts are stimulated. The abnormal gallbladder contracts are observed in this gallstone symptoms diagnosis test.
Gallbladder stones treatment
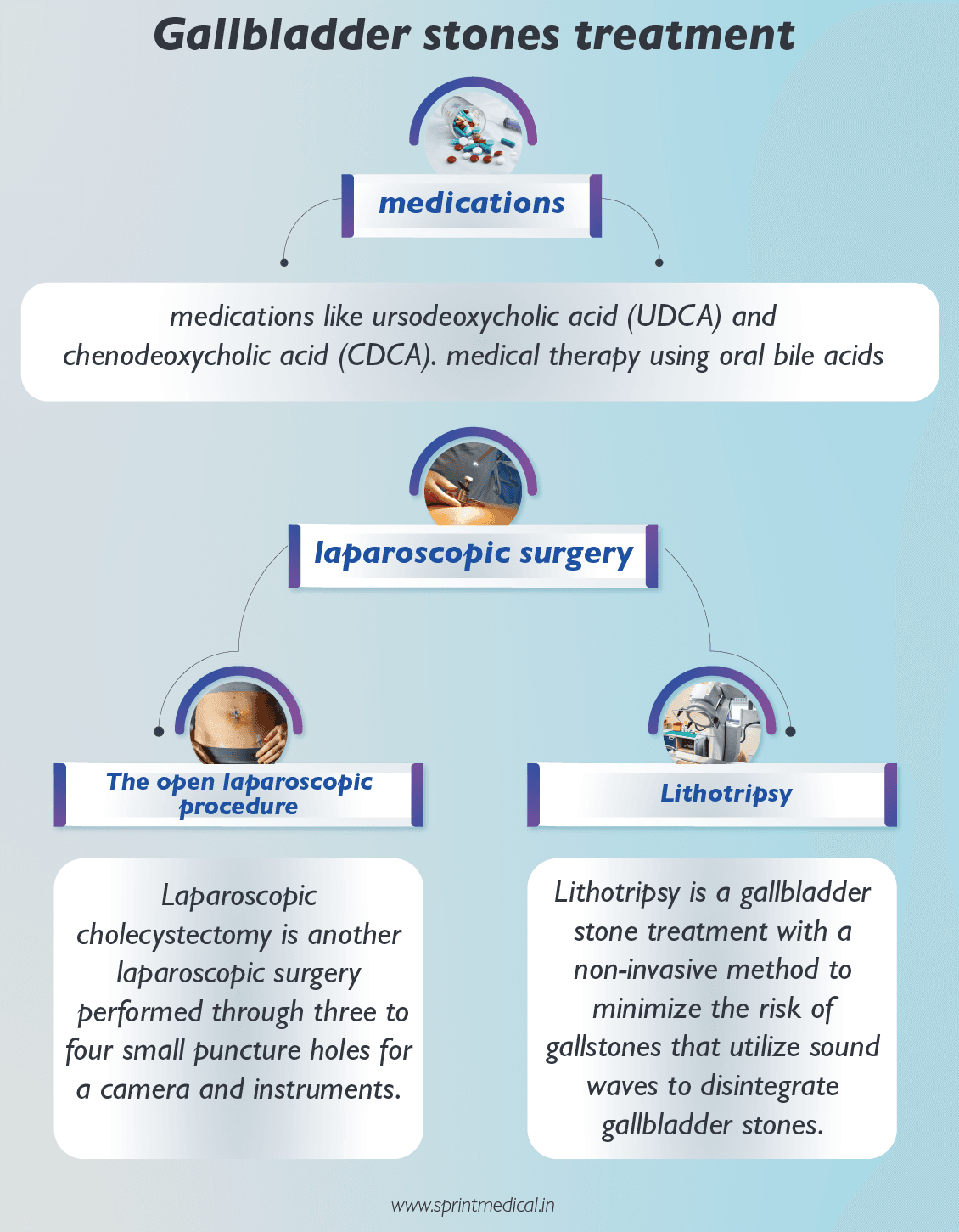
Gallbladder stones treatment includes medications, laparoscopic surgery with non-invasive and invasive methods-
Gallbladder stones treatment with medications
Gallbladder stone treatment includes medications like ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) are used in gallbladder stones treatment. It is scientifically proven that gallbladder stones treatment wth UDCA helps to prevent the formation of gallstones during weight loss.
Gallbladder stones treatment of medical therapy using oral bile acids will help to treat small gallstones and laparoscopic surgery is required for large cholesterol gallstones. Sometimes gall bladder stones treatment with CDCA will cause diarrhea, mild reversible hepatic injury, and a small increase in the plasma cholesterol level.
Gallbladder stones use in traditional medicine
Gallstones obtained as a by-product of animals that are butchered for meat are used as an antipyretic and antidote in the Chinese traditional medical culture.
Gallbladder stones treatment with laparoscopic surgery
Gallbladder stones treatment also involves gallbladder removal surgery (cystectomy) that has a 99% chance of eliminating the gallstones and preventing the formation of gallstones. Gallbladder cancer can be removed with gallbladder removal surgery (cholecystectomy) or laparoscopic surgery.
The absence of a gallbladder does not have any impact on the health of people but can lead to a post-cholecystectomy syndrome which causes nausea, indigestion, diarrhea, and episodes of abdominal pain.
There are two gallbladder removal surgery options for patients with gallstones:
Gallbladder stones treatment with the open laparoscopic procedure
The open laparoscopic procedure is done through an abdominal incision [laparotomy] below the right ribs. The recovery from this laparoscopic surgery will take 3 to 5 days of hospitalization, and with the diet of gallbladder stones, it will take a week.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is another laparoscopic surgery performed through three to four small puncture holes for a camera and instruments. Postoperative care of laparoscopic surgery includes a few days of rest and medication at home.
If bile ducts are obstructed, treatment of gallbladder stone symptoms with endoscopic retrograde sphincterotomy (ERS) followed by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) will help to reduce the risk of gallstones.
Gallbladder stones treatment with Lithotripsy
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy is a gallbladder stone treatment with a non-invasive method to minimize the risk of gallstones that utilize sound waves to disintegrate gallbladder stones. The side effects of this gallbladder stones treatment include biliary pancreatitis and liver hematoma.
Advantages of laparoscopic surgery (gallbladder removal surgery)
The laparoscopic surgery or gallbladder removal surgery of gallbladder removal involves smaller incisions, each less than one-inch length.
The laparoscopic surgery has less pain compared to open surgery.
The laparoscopic surgery allows you for easy recovery and you can perform daily activities quickly after the gallbladder removal surgery.
The procedure of laparoscopic surgery
The laparoscopic surgery of gallbladder removal starts with anesthesia injection. After you fall asleep, the laparoscopic surgery of gallbladder removal is done and 3 to 5 incisions of laparoscopic surgery are done and are closed with stitches, glue, or tape after the surgery of gallbladder removal.
The stitches of laparoscopic surgery for gallbladder removal will heal on their own. The procedure of surgery of gallbladder removal involves the insertion of a small device called a port into the incision. The Gallbladder stones treatment has a port that creates space for the surgeon to see through the camera. The camera shows the laparoscopic surgery of gallbladder removal on a screen. After the gallbladder removal surgery, the incisions are closed.
Prevention
To prevent the formation of gallstones you need to maintain a healthy diet and healthy weight. Regular exercise and sufficient fiber intake will help prevent the formation of gallstones.
Gallstones diet or Gallbladder stones diet
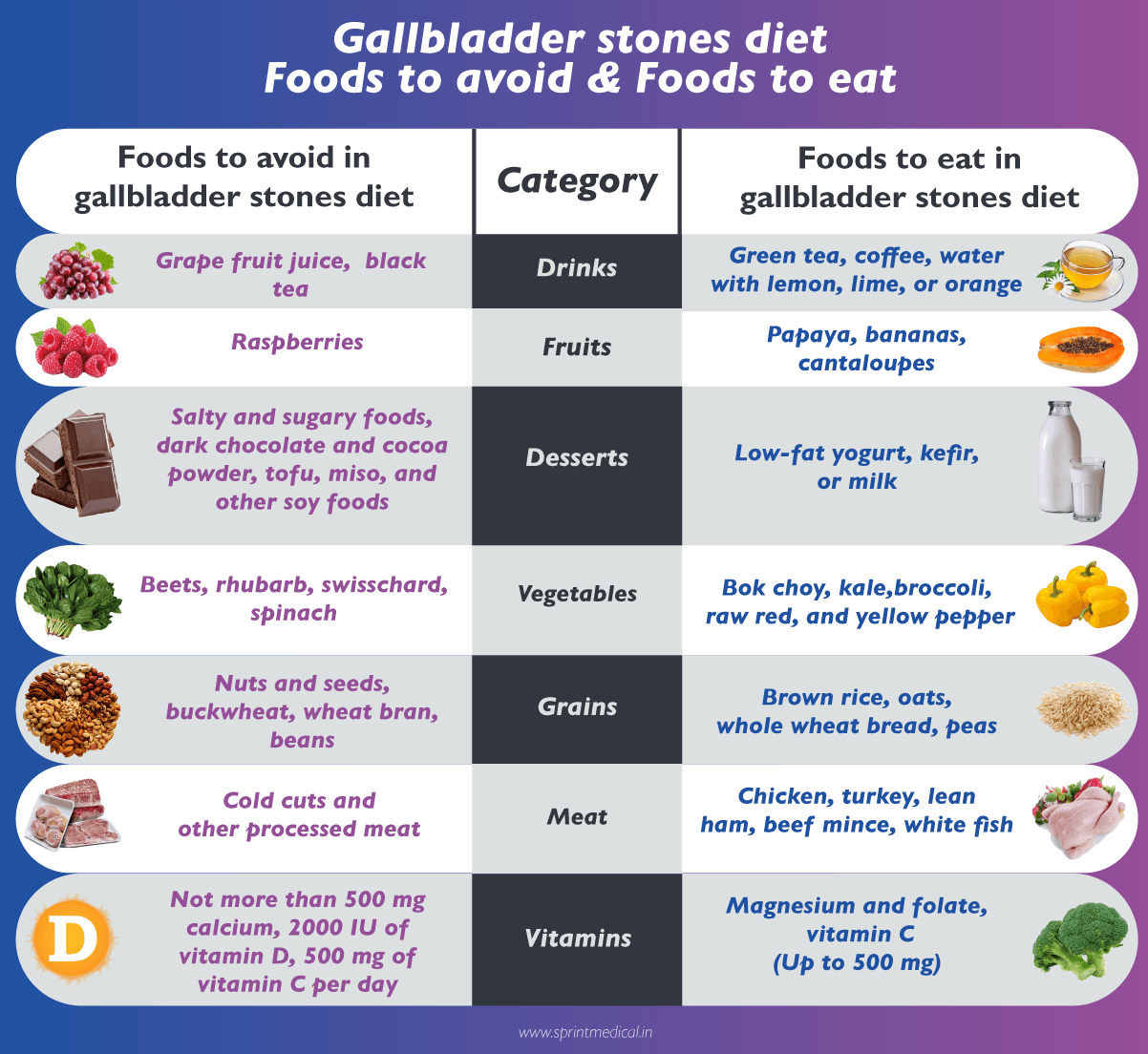
A gallstones diet or gallbladder stones diet will prevent the cause of gallstones and the formation of gallstones. Gallbladder stones diet includes a healthy and balanced gallstones diet with plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables along with whole grains.
Increase the consumption of foods that are rich in fiber, and consume only healthy fats like fish oil and olive oil to help in the gallbladder contracts. To avoid the risk of gallbladder stones symptoms you need to avoid the consumption of foods that contain high saturated fats.
The foods that contain saturated fats include red meat, sausages, fatty cuts of meat, butter, ghee, lard, cream, hard cheeses, cake, and diskettes. Also, food containing coconut or palm oil is restricted in the gallbladder stones diet as they increase the severity of gallstone symptoms.
It is scientifically proven that regular consumption of nuts, peanuts, or cashews will reduce the risk of developing gallstones or gallbladder pathri.
Foods to take during gallbladder stones diet to reduce gallstone symptoms
Take-Home Points
Gallbladder stone symptoms are caused due to increased levels of bilirubin in the common bile ducts
Gallstones are divided into cholesterol gallstones and pigmented gallstones
Gallbladder cancer can be cured if diagnosed at early stages with medications or gallbladder removal surgery
It is believed that gallstones can be prevented through a balanced diet by avoiding fatty meat, sugary foods, high-fat cheese, and lard
Gallbladder stones treatment includes medications, lifestyle changes, and surgery
Most people have asymptomatic gallstones that do not cause any pain but block the movement of bile fluids
Laparoscopic procedures are the permanent cure for people with gallstones
Increased risk of gallstones is observed in the females above 40, people with diabetes, liver disease, history of gallstones, cirrhosis, pregnant, high cholesterol diet
Gallstones or gallbladder pathri can lead to complications like acute cholecystitis, pancreatitis, and acute cholangitis
References
FAQ on Gallstones (Cholelithiasis)
Presence of diabetes, cholesterol, sickle cell disease, pregnancy, family history of gallstones, obesity, female with age above 40, rapid weight loss, fasting, cirrhosis of the liver.
Gallstones are not serious and have no symptoms in most cases. But can lead to serious problems like gallbladder infection, inflammation of the pancreas, jaundice, obstruction of bile ducts, and gallbladder tears that can lead to death.
Medications for gallbladder stones treatment will help to break the gallstones without gallbladder removal surgery. In some cases where gallbladder stones treatment with medications takes so long to work, shockwave therapy is used to break the stones. Laparoscopic surgery or gallbladder removal surgery is recommended for the permanent removal of gallstones.
Gallbladder cancer is caused if the gallbladder stones are larger or equal to 3 cm. Gallstones can be less dangerous if present less than 1 cm.
Gallstones or gallbladder pathri can be passed on their own through the common bile ducts into the excretion system if they are small in size.
If left untreated gall bladder stones can lead to complications like jaundice, acute Cholecystitis, pancreatitis, and acute cholangitis.
Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and laparoscopic surgery are recommended treatments for gallbladder cancer.
The risk of gallstones can be reduced by eating foods that contain healthy fats like fish oil and olive oil, including more fruits and vegetables, beans, and whole grains. Avoid foods that contain carbohydrates sugars and fried foods.
Comments ( 0 )
No Comments
Leave a Comment
Related Posts
Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
What is inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)? Discover the types, causes, treatments, and symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Dr. Jilas Paingeeri
Gallstones: Overview, symptoms, causes and treatment
Gallstones are asymptomatic but lead to complications like gallbladder cancer, pancreatitis. Gallbladder stones treatment includes medications, diet, and laparoscopic surgery.
Manasa Krishna Perumalla
Difference between Piles, Fissure and Fistula
Identify the difference between piles, fissure, and fistula so that you can opt for proper treatment and get relief fast.
Manasa Krishna Perumalla
Health & Wellness Tips
Subscribe to our blog