21/08/2023 / Health and Fitness
Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease: Symptoms Causes and Prevention
A very contagious viral infection that might affect your child is the Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease. Read ahead to know more about the disease.
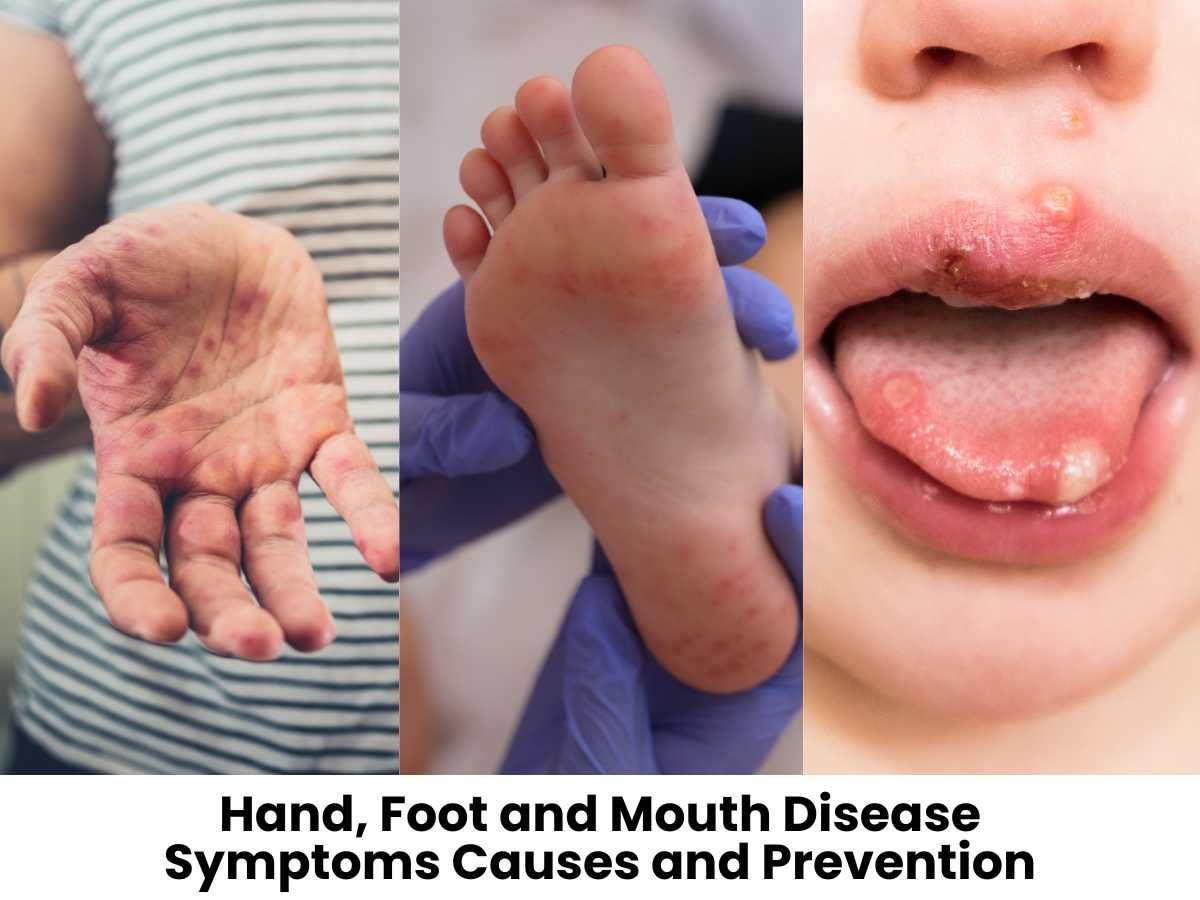
Table of Content
Introduction
A mild, infectious viral sickness that typically affects newborns and young children but can also affect adults is hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). It is brought on by an enterovirus, a virus that is extremely contagious and spreads quickly in social settings like daycares, schools, and summer camps.
The majority of HFMD patients recover fully within a week to 10 days without medical care, and the condition is typically not dangerous. Hand, foot, and mouth illness has no specific treatment. Your child's risk of infection may be reduced by routine hand washing and avoiding close contact with those. In some instances, though, HFMD can result in difficulties, especially in young infants and those with compromised immune systems.
In this article, we'll tell you more about this common viral infection.
What is the Hand Foot Mouth disease?
Hand Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a contagious viral infection that is most common in infants and young children.
The condition is very common and it causes blisters and sores. Little children tend to experience it the most frequently.
It is very easy to contract hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). It is brought on by enterovirus, a type of virus that is highly contagious and can spread rapidly in close-knit communities such as daycares, schools, and summer camps. Most frequently the coxsackievirus is found to be the cause of the condition.
Direct contact with unclean hands or feces-contaminated surfaces can cause these viruses to transfer from one person to another. Moreover, it can be spread by coming in contact with someone else's saliva, feces, or respiratory secretions.
A rash on the hands and feet and oral blisters or sores are symptoms of HFMD. Although the infection can affect persons of any age, it most frequently affects kids under the age of 5.
Usually, it's a minor condition that gets well on its own within a few days. Though the disease doesn't have any specific treatment, you should consult your doctor to rule out the possibility of another infection and to avoid complications like viral meningitis and encephalitis.
Causes of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
HFMD is caused by the enterovirus, a type of virus that is highly contagious and can spread easily from person to person.
The virus is most commonly spread through close contact with an infected person's saliva, nasal secretions, or feces. This can happen when an infected person coughs or sneezes, or when they touch a contaminated surface and then touch their mouth or nose.
The virus can also be spread through contact with blister fluid from an infected person's skin rash. However, this is less common than person-to-person transmission.
HFMD is most common in the summer and fall months, although it can occur at any time of year. The virus is more prevalent in crowded areas such as daycares, schools, and summer camps, where it can easily spread from person to person.
Transmission of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
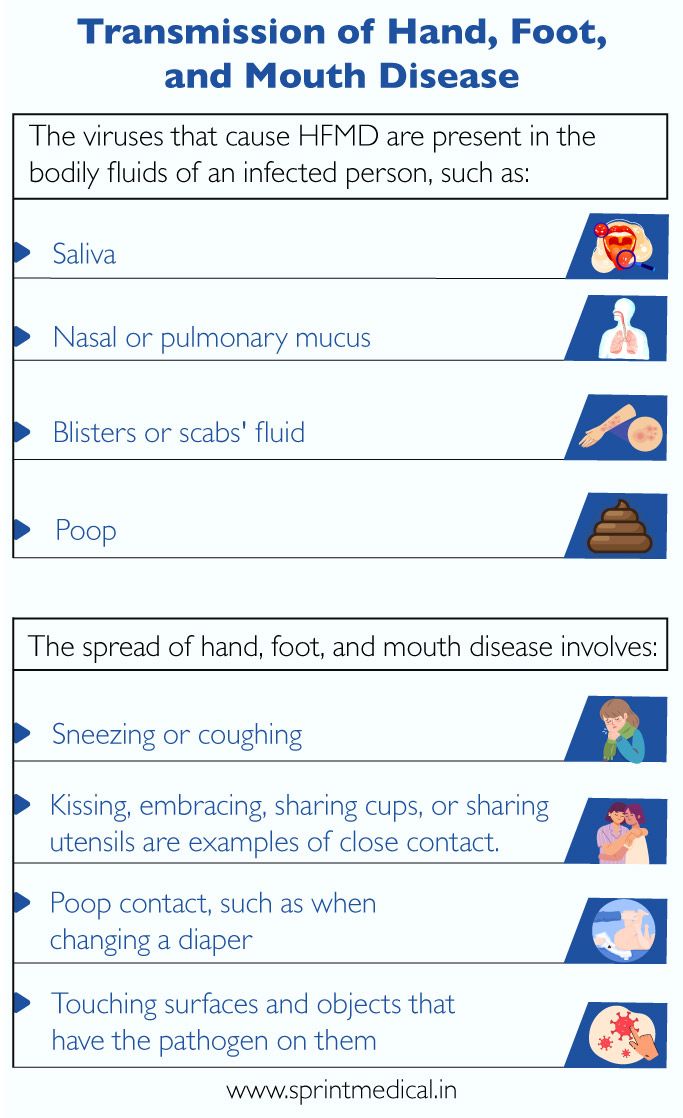
The viruses that cause HFMD are present in the bodily fluids of an infected person, such as:
Saliva
Nasal or pulmonary mucus
Blisters or scabs' fluid
Poop
The spread of hand, foot, and mouth disease involves:
Sneezing or coughing
Kissing, embracing, sharing cups, or sharing utensils are examples of close contact.
Poop contact, such as when changing a diaper
Touching surfaces and objects that have the pathogen on them
Symptoms of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
After getting the infection, symptoms start to appear 3 to 6 days later. Incubation is the term used to describe this time frame. You or your child may suffer any of the following when symptoms do arise:
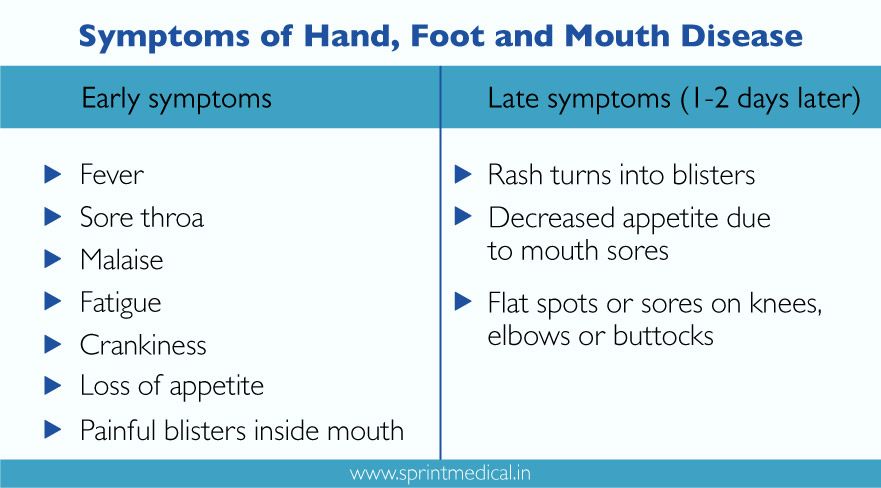
fever
decreased appetite
sore throat
headache
irritability
malaise (feeling unwell)
painful red blisters in your mouth
drooling
a red rash on your hands and the soles of your feet
A mouth sore may make swallowing painful. The only indication that a youngster is ill could be that they are eating or drinking less than normal. Make sure they receive adequate nutrition and liquids.
Usually, the rash appears as flat, red patches. Darker skin tones can make the spots difficult to discern, so it's easier to inspect the bottoms of the feet and the palms of the hands, where the condition might be more obvious.
Although lesions can develop on any part of your hands or feet, this is one of the few instances where you will notice a rash on your palms and soles, making it simple to spot.
The majority of kids with HFMD also experience uncomfortable mouth sores. Examine their neck and tongue, particularly the sides.
Prevention of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
The first seven days of your child's illness are when they are most contagious. Yet, the virus can persist in their bodies for days or even weeks and transmit via spit or feces. Take the following actions to reduce the risk of infection:
Carefully wash your hands, especially after changing a child's diaper or wiping their nose. Encourage kids to wash their hands.
Instruct young children to cover their mouth and nose when they cough or sneeze. The ideal thing to use is a tissue, although their shirt's sleeve also works.
Surfaces, shared goods like toys, and doorknobs should all be cleaned and disinfected.
A person who has HFM should not be hugged or kissed. Share no drinks or eating utensils with them.
Send your child to daycare or school only when their symptoms have subsided. If you believe they might still be contagious, consult your doctor.
Treatment of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
The Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease is a very common and infectious viral infection that affects all ages. Even though the disease self heals over a period of a few (7-10) days, you must consult a doctor. Symptomatic treatment can be done to relieve the pain and suffering of the patient. Fever can be treated with antipyretic medications like acetaminophen and aspirin. Though aspirin must be avoided in patients of Reye's disease. For sore throat lozenges can be given. There is no specific treatment for the disease.
When to consult your physician?
Typically, hand, foot, and mouth disease is a minor condition. Usually, it only results in a few days of fever and minor symptoms. If your kid is younger than six months old, has a compromised immune system, mouth sores, or a sore throat that makes it uncomfortable to take fluids, call your healthcare practitioner right away. If your child's symptoms don't go better after 10 days, call your doctor as well.
Your child is not drinking enough to stay hydrated.
After 10 days, the symptoms have not subsided.
Your child's immune system is compromised; the symptoms are severe
Your child is really young, particularly if they are under six months old.
Take-Home Points
Hand foot and mouth disease is a common and highly contagious disease caused by several viruses. While it is generally mild, it can cause uncomfortable symptoms including fever, sores, and blistering all over the body. It is important for those who have been infected to rest, drink plenty of fluids and avoid contact with others until all the symptoms have gone away to prevent further spread of the disease. In conclusion, hand foot and mouth disease can affect anyone and is easily spread, however, it is usually quite mild and can be treated easily.
References
FAQ on Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
The HFMD affects all age groups. Though it is more common in kids, it also affects adults.
The virus of HFMD can survive on surfaces for many days.
Yes, the HFMD can spread through air via small droplets.
HFMD is a very contagious disease and you should practice isolation of the patient till the blisters have completely healed.
HFMD is highly contagious and can be spread through close contact with infected individuals, as well as through contact with contaminated surfaces or objects.
You should avoid acidic and citrus foods and drinks if suffering with HFMD.
The best way to prevent HFMD is to practice good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and thoroughly, disinfecting surfaces and objects, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
Vaccines for HFMD are not currently available.
Comments ( 0 )
No Comments
Leave a Comment
Related Posts
Chia Seeds Benefits for Skin
When it comes to gleaming and healthy skin, it all comes down to the food we eat. Antioxidants play a major role in determining the age of a cell so does the glow of the skin. Using chia seeds for skin can be a good pick, it has all the antioxidants.
Mohammad Aqdus
Best fruit and vegetable juices for healthy and glowing skin
Care for your skin, care for your beauty. Here is the way to love your skin naturally.
Juveriya Anwar Momin
Legionnaire Disease: Symptoms, Causes and treatment
Discover the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of Legionnaires disease, a severe form of pneumonia caused by Legionella bacteria.
Dr. Mrinalinee Roy
Health & Wellness Tips
Subscribe to our blog