Natural ways to manage Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-lasting disease that interferes with your lifestyle, which you can manage easily with a simple understanding and changes in your diet and lifestyle.

Table of Content
What is diabetes?
It is a chronic (long-lasting) degenerative disease caused by the imbalance of hormones and its related disturbances in metabolism. This is characterized by elevated blood glucose levels that can damage your heart, kidney, eyes, and nerves. The most common diabetes is type-2 diabetes.
Diabetes is a major cause of blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, stroke, and lower limb amputation. The risk of diabetes is influenced majorly by ethnicity, race, age, history, and physical inactivity.
Why is diabetes so common?
The diabetes burden is increasing globally and especially in developing countries like India. As a result of obesity and lack of physical activity, it is so common nowadays.
The statistics are alarming; 30 million people were diagnosed with diabetes worldwide in 1985, by 1995 the numbers increased to 135 million, and at the current rate, there will be around 300 million diabetics by the year 2025 as predicted by the WHO.
As per the estimated data, around 77 million Indians were diabetic in 2019. This might rise to 134 million by 2045. A large population is suffering from type 2 diabetes.
The WHO has estimated that diabetes will be one of the world’s leading causes of death and disability in the next quarter century.
What are the types of Diabetes?
Yes, there are types of diabetes. It is a disease consisting of hyperglycemia and an increased risk of eye and kidney damage.
There are three types of diabetes
1. Type1- diabetes mellitus/ insulin-dependent diabetes
It was once called juvenile diabetes. Most commonly develops in children, teens and adults. Type 1 diabetes refers to a total of 5% of total diabetic patients.
Less common than type 2 diabetes. It is autoimmune where insulin-producing beta cells are destroyed.
2. Type 2- diabetes insipidus/non-insulin dependent diabetes
This is mostly seen in people over 45, but children and teens are also developing it. Here cells do not respond to insulin.
3. Type 3- gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy
This occurs when your body is unable to make enough insulin during pregnancy. All pregnant women have some insulin resistance during late pregnancy.
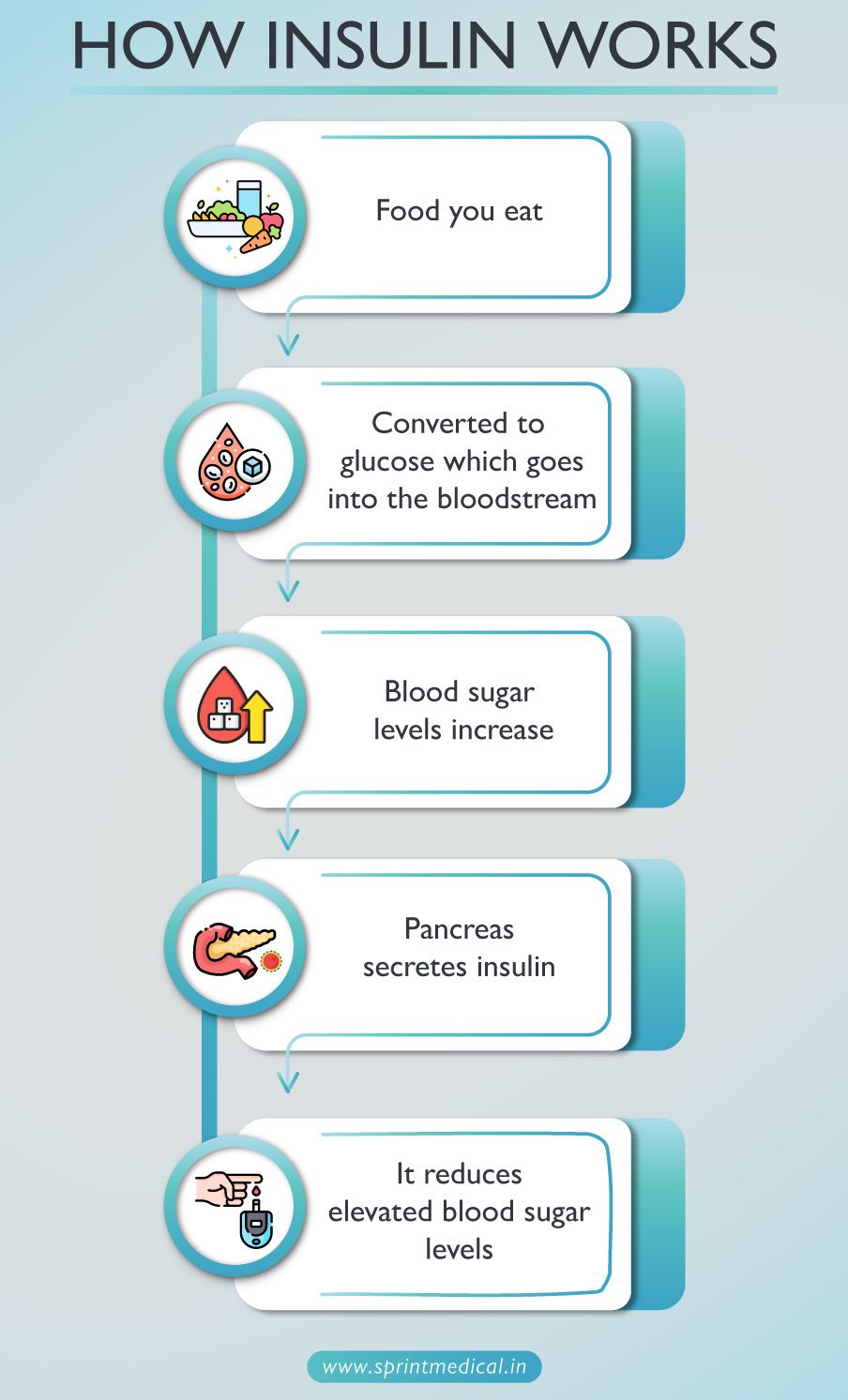
How insulin works
With diabetic patients, the body does not make enough insulin or cannot use it properly.
Is Diabetes curable?
Diabetes is not curable, but you can lose weight, change your eating habits, be active daily and take your prescribed medications to manage diabetes.
Living with diabetes is not easy but it is manageable.
Treatment options for diabetes
Once the diabetes is confirmed patient has to follow the treatment as per the physician’s guidelines, which includes-
1. Diet
2. Physical activity
3. Tobacco cessation
4. Blood glucose monitoring
5. Blood lipid control
6. Medical management:
For type 2 diabetes treatment includes medication and physical exercise which varies with your age, weight, and sex.
There are different drugs for diabetes management, which work in different ways to lower your blood glucose levels. Most of the time doctors may prescribe you a combination of drugs.
For type 1 diabetes, a doctor will prescribe you insulin.
Food to always choose with diabetes

These are the food options you can choose with no worries.
Vegetables
Cucumber, broccoli, cauliflower, spinach, bitter gourd (karela) carrots, green beans, cabbage, sweet potato, and artichoke.
Fruits
Bananas, apples, grapes, pears, peaches, oranges, melons, grapefruit, kiwi, berries, tomato, oranges and dates.
Grains
High-fiber cereals, corn, oatmeal, pasta, wheat, millet, barley.
Legumes
Kidney beans, black beans, peas, lentils, non-fat soy products.
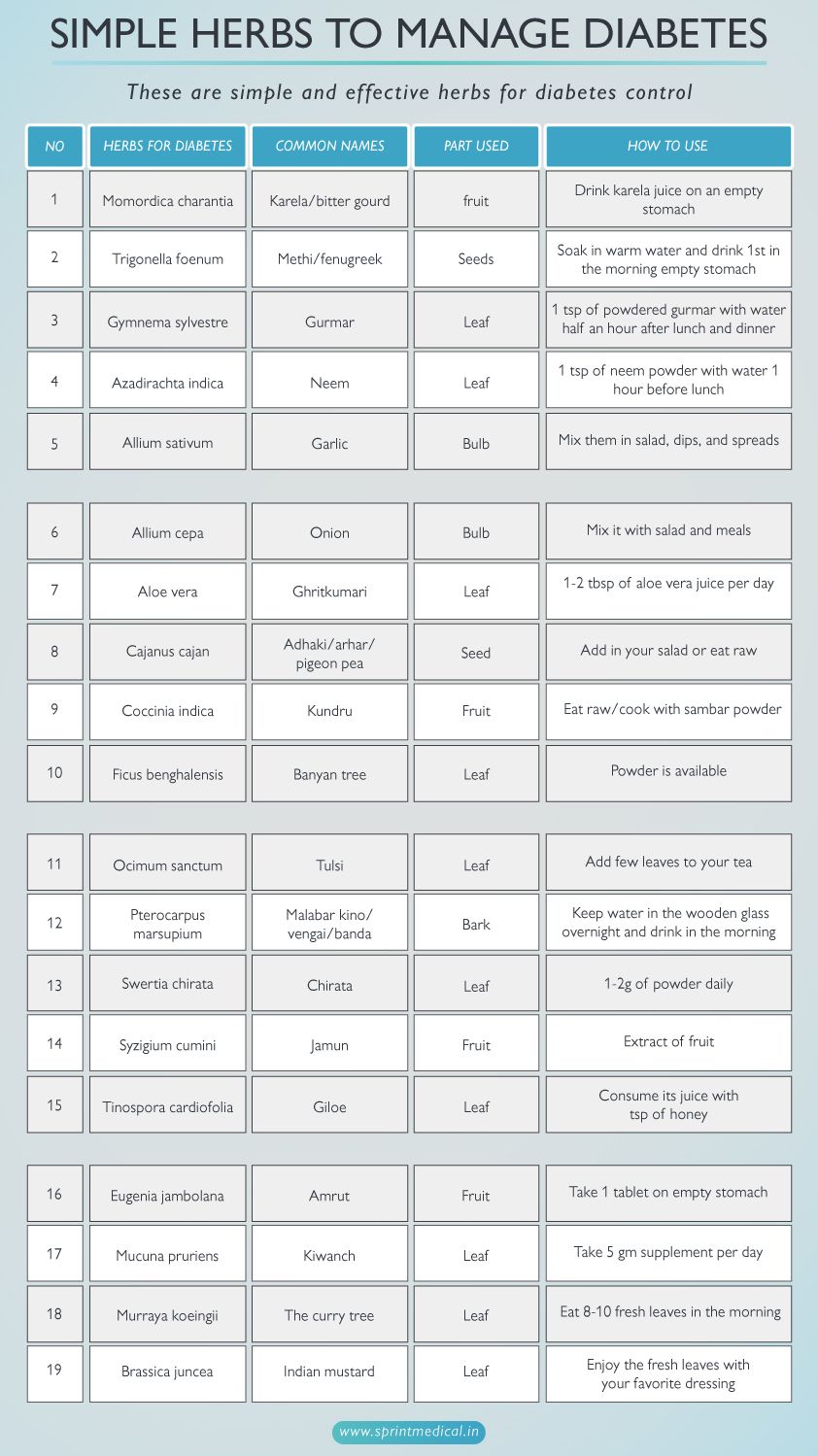
Simple Herbs to manage diabetes
These are simple and effective herbs for diabetes control.
Dietary supplements for decreasing glucose levels
These are two supplements that play a major role in insulin action regulation
1. Chromium

Chromium is an essential trace element that regulates all the activities of insulin and maintains the blood glucose level.
Without chromium, insulin action is blocked. It helps to-
Decreases fasting glucose levels.
Improve glucose tolerance.
Lower insulin levels.
Increases High-Density Lipoprotein (good cholesterol)
Foods rich in chromium
Grape juice
Orange juice
Pancakes
Apple with peel
Banana
Whole wheat bread
Ketchup
Peanut butter
2. Magnesium
It functions as an essential cofactor for more than 300 enzymes. Its deficiency is one of the causes of diabetes

Foods rich in magnesium
Pumpkin seeds
Chia seeds
Dry roasted almonds
Boiled spinach
Dry roasted cashew
Soymilk, plain milk
Black bean
Baked potato with skin
Plain yogurt
Instant oatmeal
Kidney bean
Raisins ½ cup
Salmon cooked
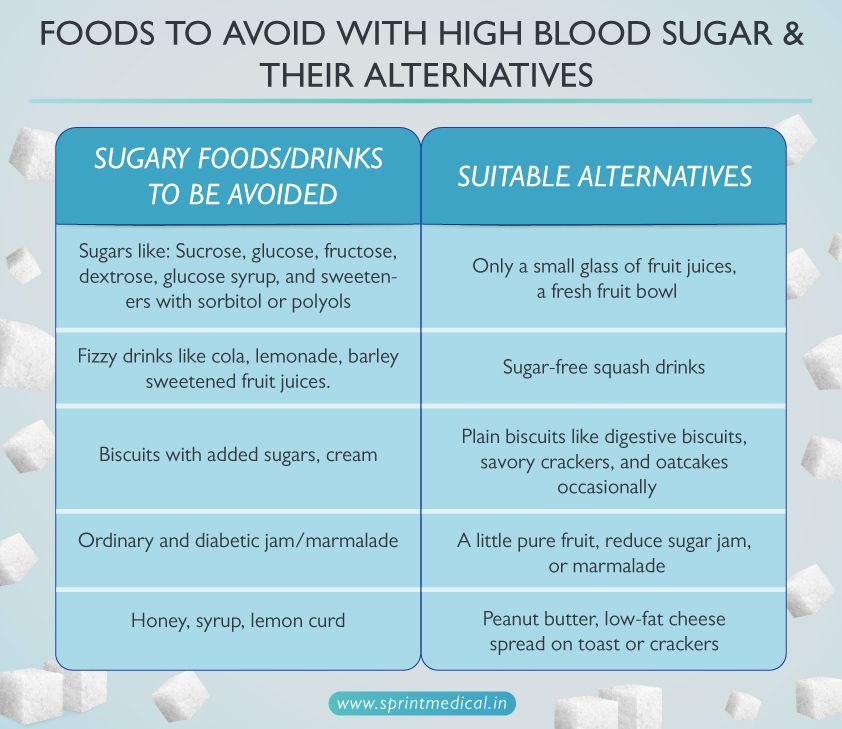
Foods to avoid with high blood sugar and their alternatives
How to reduce sugar levels at home
A healthy diet, and maintaining a healthy weight with regular physical activities can help you. Other options are:
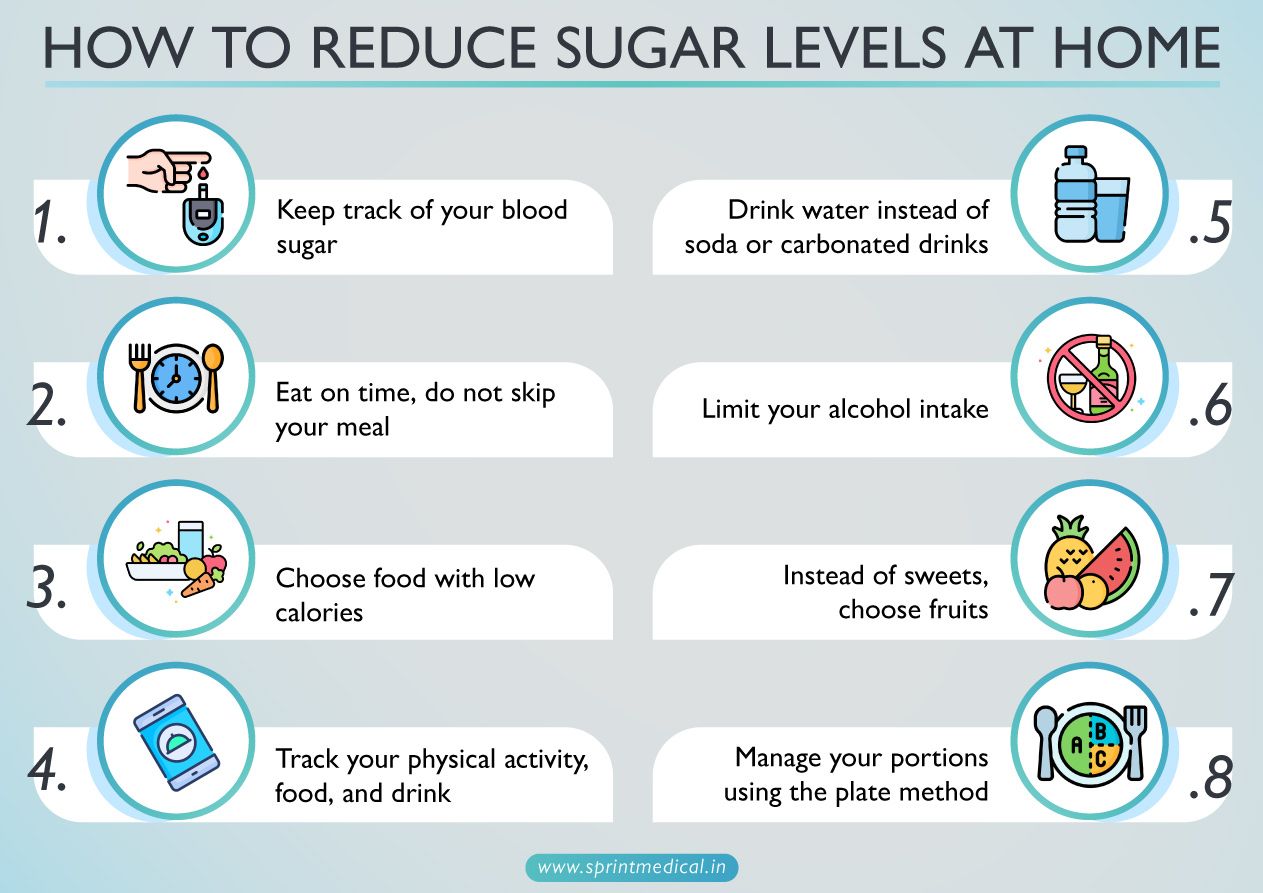
Keep track of your blood sugar.
Eat on time, do not skip your meal.
Choose food with low calories.
Track your physical activity, food, and drink.
Drink water instead of soda or carbonated drinks.
Limit your alcohol intake.
Instead of sweets, choose fruits.
Manage your portions using the plate method
The plate method is simple and visually appealing to make sure that you get the required nutrients and portions. This limits the higher-carbohydrate foods you eat that have the highest impact on your blood sugar.
Start with a 9-inch plate:
Fill half of your plate with non starchy vegetables such as salad, broccoli, cabbage, and carrots.
Add one-quarter of lean protein, like chicken, beans, eggs, etc.
Add one-quarter with high carbohydrate foods like grains, rice, pasta, fruits, beans, and yogurt.
Then choose water or a low-calorie drink such as unsweetened iced tea to go with your meal.
Take-Home Points
Diabetes is a chronic disease that has no cure but can be easily managed with simple lifestyle changes.
Make your own diet plan as per your body’s needs and follow it.
Do not skip a meal, whether it is breakfast, lunch, or dinner. Follow a routine with a good amount of sleep.
Eat healthily and eat proportionately.
Track your insulin levels before and after a meal.
References
FAQ on Natural ways to manage Diabetes
Take the prescribed medication on time, and follow a routine. Give 1 to 2 hours daily for your body, and exercise daily. Do not skip a meal, and have a good amount of sleep.
Take a brisk walk, be more active, and take the prescribed medicine. Drink water, and juice.
How often you check your blood sugar depends on the diabetes type you have and if you take any diabetes medicines.
Typical times to check your blood sugar include:
When you first wake up, before you eat or drink anything.
Before a meal.
Two hours after a meal.
At bedtime.
A blood sugar target is a range you try to reach as much as possible. These are typical targets:
Before a meal: 80 to 130 mg/dL.
Two hours after the start of a meal: Less than 180 mg/dL.
Your blood sugar targets may be different depending on your age, any additional health problems you have, and other factors.
Carbs in food make your blood sugar levels go higher after you eat them than when you eat proteins or fats. You can still eat carbs if you have diabetes.
The amount you can eat and stay in your target blood sugar range depends on your age, weight, activity level, and some other factors.
Comments ( 0 )
No Comments
Leave a Comment
Related Posts
Type 1 diabetes: How to tackle the disease in children
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition that usually appears in adolescence when the pancreas makes little or no insulin.
Dr. Jilas Paingeeri
Berries and Diabetes: List of Berries for Diabetics to Eat
Berries don't cause as much of a spike in blood sugar as other fruits. These berries are also rich in fibre. We will learn more about berries and diabetes in this article.
Sayandeep
Health & Wellness Tips
Subscribe to our blog