16/04/2022 / Gynecology and Motherhood
Endometrial Thickness: What is Normal Size of Endometrium in mm?
Understanding the Normal Range of Endometrial Thickness, Track Your Endometrial Health with Our Endometrial Thickness Chart.
Table of content
Endometrial Thickness Chart - What is Normal Size of Endometrium in mm?
4 Major Conditions That Can Cause A Change In The Endometrial Thickness Range
FAQ on Normal Endometrial thickness, measurement, changes and treatment
What is Endometrium?
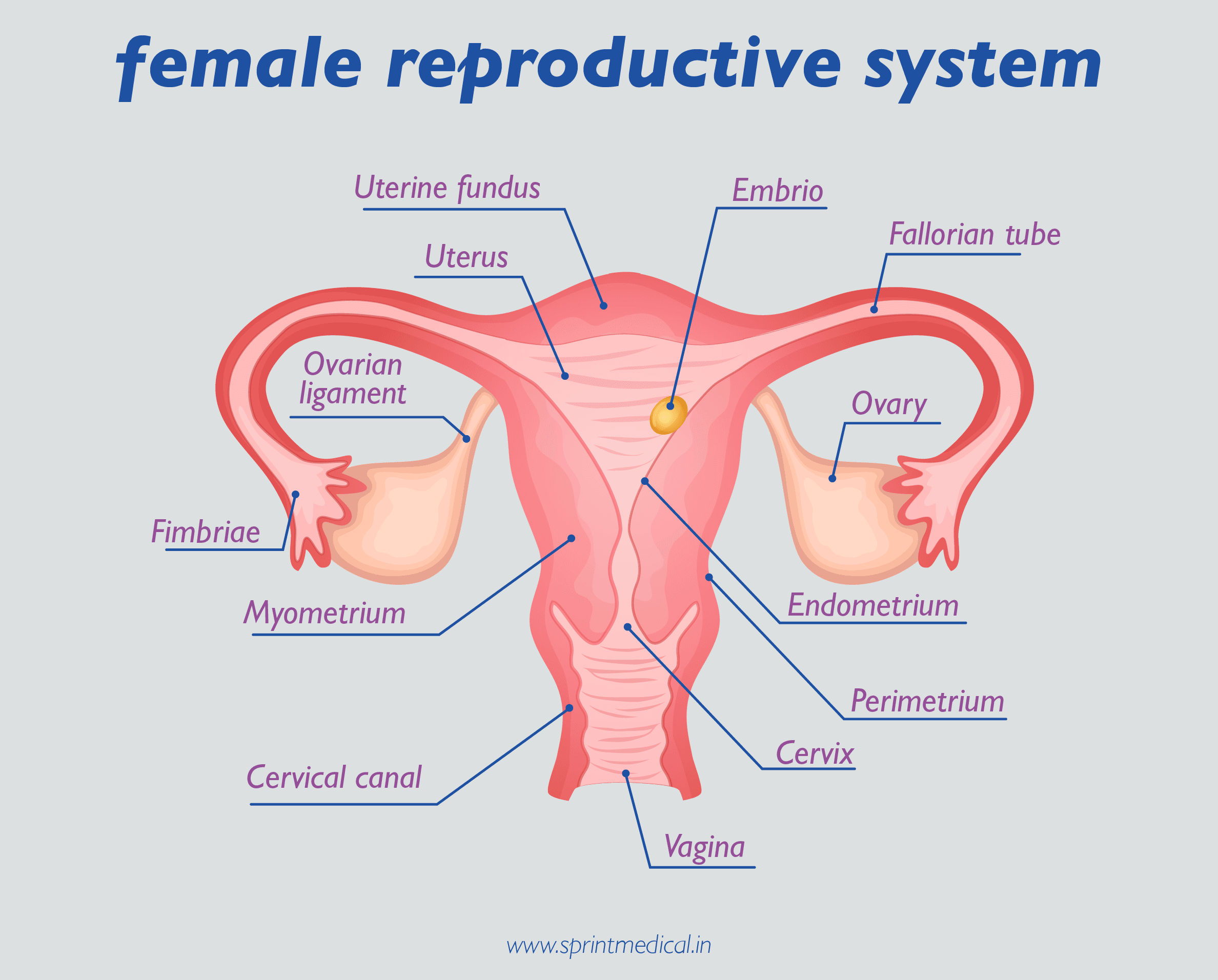
The endometrium is the inner lining of the mammalian uterus. The endometrium is an inner epithelial layer of the uterus along with its mucous membrane that has a basal and functional layer.
The layer that thickens and sheds during menstruation is a functional layer of the endometrium. Most mammals including humans shed endometrium during the menstrual cycles. In other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle.
The normal thickness of endometrium varies throughout the menstrual cycle. Regular monitoring of the endometrial thickness is important for women undergoing fertility treatment or those experiencing abnormal bleeding.
Functions of the Endometrium
The endometrium is an important part of the female reproductive system that plays a major role during the menstrual cycle, pregnancy outcome, and in postmenopausal women. The endometrial thickness range is changed during these stages.
While you are in a menstrual cycle, the endometrium grows to a thick, blood vessel-rich, glandular tissue layer which result in a change in the normal thickness of endometrium. This occurs in the anticipation of the implantation of a blastocyst in the uterus.
The endometrium thickness range is increased in size and number of glands and blood vessels during pregnancy. During pregnancy, the fusion of vascular spaces forms the placenta, to supply oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.
In postmenopausal women, the endometrial thickness must be no thicker than 4-5 mm. If endometrial thickness ranges more than this, endometriosis occurs.
Endometrial Thickness Chart - What is Normal Size of Endometrium in mm?
The thickness of the endometrium ranges depending on the phases of women. The normal endometrial lining thickness chart that is accepted is measured through transvaginal ultrasound or transvaginal ultrasonography. The normal size of the endometrium is measured in mm.
An endometrium normal size can also vary based on factors such as hormonal imbalances, obesity, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). These conditions can result in thicker or thinner endometrial linings outside of the normal range. Other factors that can affect endometrial thickness include medication use, such as hormone replacement therapy (HRT), or intrauterine device (IUD) placement.
Here is the endometrial thickness chart in different stages of women:
Endometrial Thickness Chart Normal Size (in mm) During Premenopausal Stage
The normal size of endometrium in mm during the menstrual phase of pre-menopausal women ranges from 2-4 mm. During the early proliferative stage, the endometrium normal size (in mm) increases to 5-7mm. The endometrial thickness range during the last proliferative or pre-ovulatory phase is up to 11 mm. During the secretory phase, the endometrial lining thickness is 7-16 mm.
The normal size of endometrium in mm during the pre-menopausal stage varies at different stages of the menstrual cycle.
The thickness of the endometrium in the ovarian cycle phases like menstrual phase, follicular phase, luteal phase, ischemic phase is as follows:
The endometrial thickness if present less than 14mm is considered normal in the menstrual cycle. While a woman is in hormonal therapy, the endometrial thickness reaches up to 15mm.
The endometrial thickness range following dilatation and curettage or spontaneous abortion is less than 5 mm. If the endometrium is thicker than 5 mm after abortion or delivery, consider it as remnants of conception or labor.
The endometrial thickness will be decreased with the long-term use of oral contraceptive pills.The menstrual cycles and ovarian response are responsible for clinical pregnancies.
Endometrial Thickness Chart Normal Size (in mm) During Postmenopausal Stage

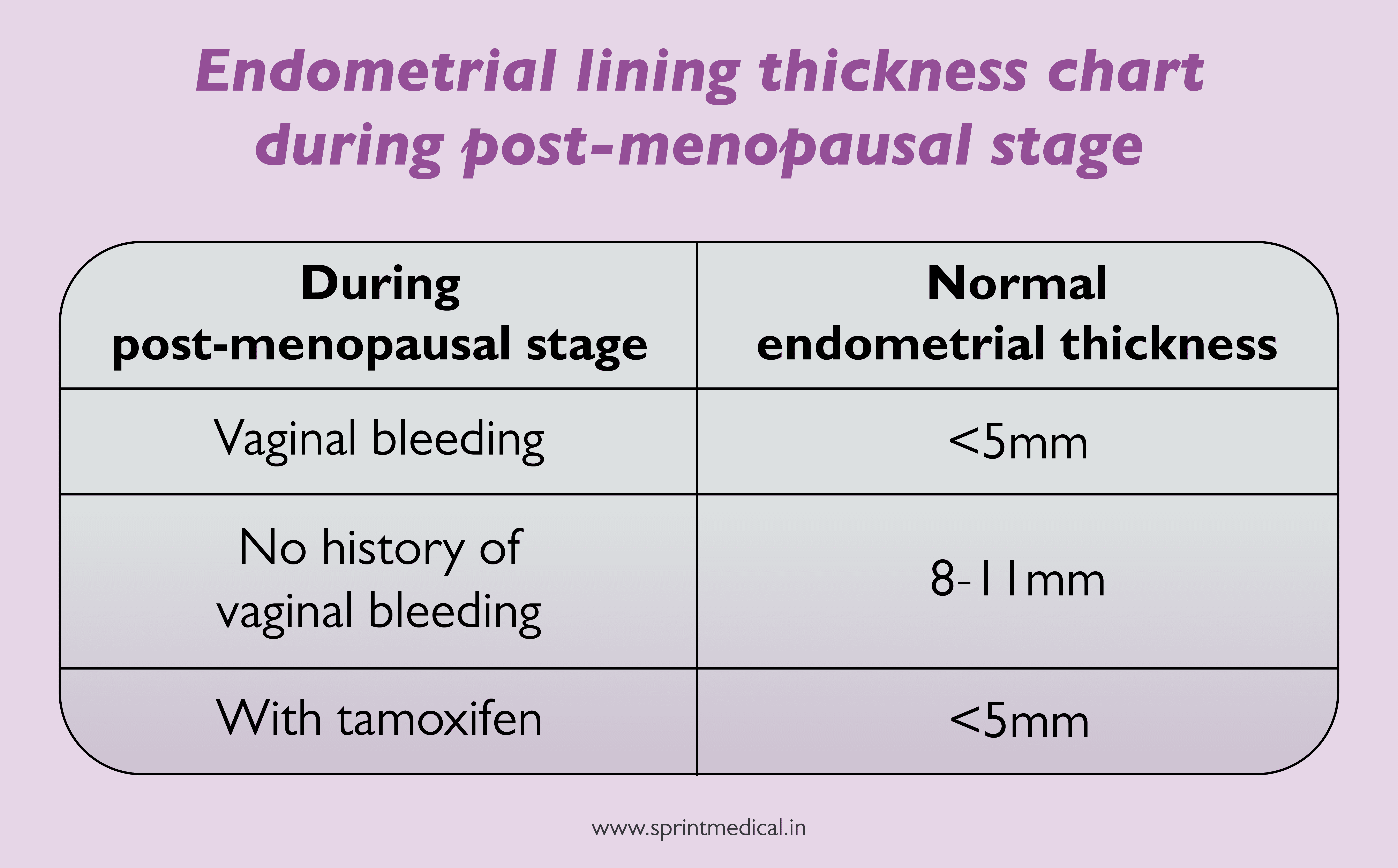
The endometrial thickness normal range can also differ for postmenopausal women. The normal endometrial thickness in mm should be less than 5 mm for post-menopausal women. If the postmenopausal endometrial thickness varies from this measurement further evaluation is needed.
The endometrial thickness range during vaginal bleeding (not on tamoxifen):
The upper limit of normal endometrial thickness is < 5mm
If the endometrial thickness range is > 5 mm, there can be a risk of carcinoma (~ 7%), and 0.07% risk, if the endometrial thickness range is < 5mm.
On hormonal replacement therapy, the normal size of endometrium in mm: upper limit of normal endometrial thickness in mm is 5mm.
The normal size of endometrium in mm- with no history of vaginal bleeding:
The acceptable normal size of endometrium in mm is suggested as 8-11
If the endometrial thickness range is > 11 mm, there can be a risk of carcinoma (~ 7%), and 0.02% risk, if the endometrial thickness range is < 11 mm.
The normal endometrial thickness with tamoxifen:
The normal size of endometrium in mm with tamoxifen is < 5 mm.
If the endometrial thickness is increased without any vaginal bleeding or uterine bleeding a transvaginal ultrasound or a consultation with a gynecologist is reasonable.
Endometrial Thickness Chart Normal Size (in mm) During Pregnancy
A normal endometrial thickness for pregnancy is required for having a normal pregnancy. It helps the embryo to get implanted and also gets the nutrition it needs to grow.
The endometrium thickness in pregnancy thickens during the later phase of pregnancy. The normal endometrial thickness for pregnancy is around 8 to 15 mm.
During pregnancy, the endometrial thickness increases to support the growing fetus. Ultrasound is the most common method used to measure endometrial thickness during pregnancy. The endometrial thickness varies depending on the gestational age during pregnancy. The endometrial thickness during pregnancy increases gradually throughout the first trimester, and then plateaus in the second and third trimesters.
The endometrial thickness varies from person to person and there are many factors that affect it. It has been seen for a lady to conceive a baby and for the pregnancy to continue, the endometrial thickness needs to be at least 15mm or more.
Endometrial Thickness Using MRI
Normal endometrial thickness and size is well assessed on MRI. The measurement of endometrial thickness should be taken at a mid-sagittal slice, the same as the transvaginal ultrasound assessment plane.
Until now you have learned about how thick the endometrium should be, the endometrial thickness chart should be in different phases. But how to measure the endometrial thickness?
How to Measure Normal Endometrial Thickness?
The thickness of the endometrium should be measured on the long axis or sagittal plane, ideally on transvaginal ultrasonography through the endocervical canal. The measurement is the biggest echogenic area from one basal endometrial interface across the endometrial can all of the other basal endometrial surface. Proper care should be taken to not include hypoechoic myometrium or intrauterine fluid in this measurement.
Measurement of Endometrium Thickness Range
Ultrasound diagnostic procedure is used to measure the normal endometrial thickness or for diseased endometrial thickness. Transvaginal ultrasound is also used to examine the situation when you experience any vaginal bleeding.
An MRI is recommended by obstetrics and gynaecology doctors if your position of the uterus or other problem makes it difficult for an ultrasound.
4 Major Conditions That Can Cause A Change In The Endometrial Thickness Range
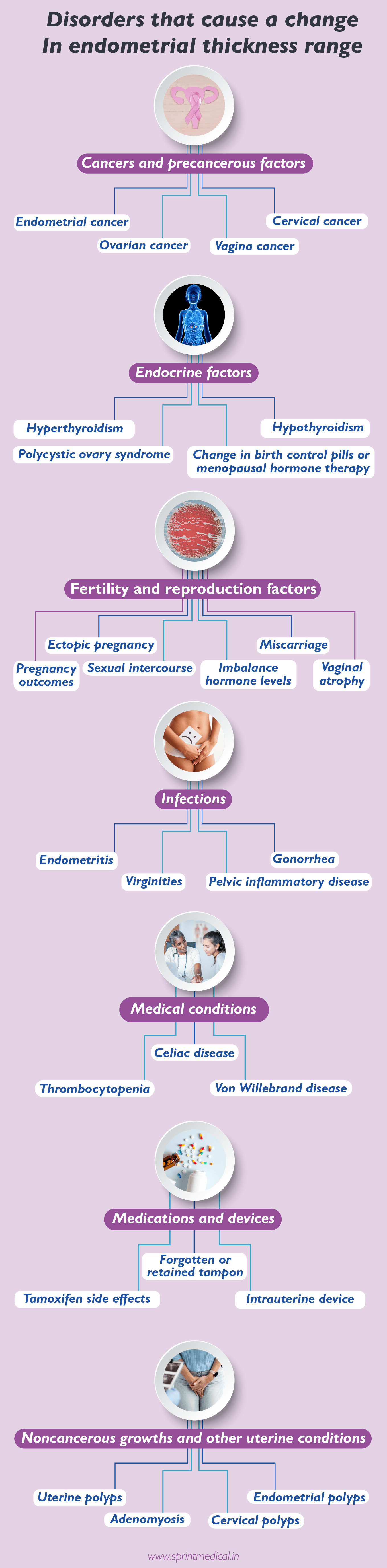
The common cause of changes in normal endometrial thickness is due to variation in the hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. These hormones regulate the menstrual cycles and pregnancy of women. The change in these hormones causes disease symptoms like vaginal bleeding or uterine bleeding,endometrial hyperplasia, endometrial cancer, endometrial receptivity.
1. Vaginal bleeding
Vaginal bleeding during menstrual cycles is normal. Abnormal vaginal bleeding is different from the menstrual cycle that comes monthly. The abnormal vaginal bleeding includes bleeding that happens before puberty or after menopause. The causes of abnormal vaginal bleeding include:
Cancers and precancerous factors
Endometrial cancer
Cervical cancer
Ovarian cancer
Vagina cancer
Endocrine factors
Hyperthyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Change in birth control pills or menopausal hormone therapy
Fertility and reproduction factors
Sexual intercourse
Imbalance hormone levels
Ectopic pregnancy
Miscarriage
Pregnancy outcomes
Vaginal atrophy
Infections
Endometritis
Gonorrhea
Virginities
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Medical conditions
Celiac disease
Thrombocytopenia
Von Willebrand disease
Medications and devices
Forgotten or retained tampon
Tamoxifen side effects
Intrauterine device
Noncancerous growths and other uterine conditions
Adenomyosis
Cervical polyps
Uterine polyps
Endometrial polyps
Trauma blunt trauma or penetrating injury to the vagina or cervix, sexual abuse.
Treatment of vaginal bleeding
Depending on the underlying cause the treatment of vaginal bleeding is determined. The necessary for the treatment is also decided based on the severity. In many cases, the cause of vaginal bleeding such as thyroid, liver, kidney, or blood clotting problems is treated with medications.
Medications for the treatment of irregular vaginal bleeding include
If the cause of vaginal bleeding is lack of ovulation, use of progesterone to be taken regularly or an oral contraceptive with progesterone is suggested.
If the cause of vaginal bleeding is a precancerous change, progesterone medications are prescribed to reduce endometrial cancer to avoid surgery.
In postmenopausal women or women at the stage of menopause, an oral contraceptive is prescribed for a regular vaginal bleeding pattern and to relieve hot flashes.
If vaginal bleeding is due to polyps or due to benign tumors, a surgical procedure is advised as medication cannot treat this.
If the infection is the cause of vaginal bleeding, antibiotics are used. If the bleeding is observed during pregnancy, an evaluation is conducted and if reported as endometriosis medications or surgery is carried out.
If the medications are unable to control the vaginal bleeding, then a surgical procedure is necessary.
Hysterectomy is occasionally required when hormonal medications cannot control excessive vaginal bleeding.
2. Endometrial hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition where an excessive proliferation of endometrial cells occurs. Endometrial hyperplasia is caused due to increased levels of estrogen and due to insufficient levels of progesterone-like hormones that will counteract the estrogen effect on the proliferation of endometrium tissue. An endometrium normal size is crucial in diagnosing endometrial hyperplasia.
Endometrial hyperplasia may occur due to obesity, polycystic ovarian syndrome, tumors that produce estrogen, or intake of compounds for estrogen replacement therapy. Endometrial hyperplasia may cause or coexist with endometrial cancer.
The endometrial lining thickness will change during endometrial hyperplasia. The thin uterine lining will become unusually thick because of the increased cell number.
Endometrial hyperplasia is classified into 4 types as per World Health Organization; these include -
Simple hyperplasia without atypia
Complex hyperplasia without atypia
Simple atypical hyperplasia
Complex atypical hyperplasia
Later the classification of simple and complex was removed and was distinguished only as presence and absence of atypia.
Endometrial hyperplasia- Irregularity and cystic expansion of glands and budding of glands which leads to change in the appearance of individual glands. This type of endometrial hyperplasia will develop into endometrial cancer eventually. In a retrospective cohort study, 1.6% of patients with endometrial hyperplasia symptoms have eventually developed endometrial cancer.
Atypical endometrial hyperplasia- simple or complex architectural changes with atypical changes England sales that include cell stratification, tufting, loss of nuclear polarity, enlarged nuclei, and increase in meiotic activity. All these changes in the atypical endometrial hyperplasia or similar to true cancer cells but do not show any invasion into the connective tissue which is the defining characteristic of cancer. In a retrospective cohort study, 22% of patients with atypical endometrial hyperplasia have shown endometrial cancer occurrence.
Endometrial hyperplasia is diagnosed through ultrasound or transvaginal ultrasonography, biopsy, hysteroscopy. It is essential to monitor the endometrial thickness and endometrium normal size in mm to diagnose and treat endometrial hyperplasia.
The thickened endometrium treatment depends on the severity and type of hyperplasia. For simple hyperplasia, hormonal therapy is usually the first line of treatment. This may involve taking progestin to balance out the effects of estrogen. In contrast, complex hyperplasia with atypia, a more severe form of the condition, often requires surgery, such as a hysterectomy, to remove the uterus.
You need to consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
Vagina bleeding
Uterine bleeding
Painful urination
Missed menstrual cycles
Endometrial thickness treatment in endometrial hyperplasia
Endometrial thickness treatment involves hormonal therapy, such as cyclic or continuous progestin therapy, or hysterectomy.
3. Endometrial cancer
Endometrial cancer is cancer that occurs in the uterus causing thick endometrial lining. It usually occurs due to the abnormal growth of cells that can invade or spread to other parts of the body. The first symptom of endometrial cancer is vaginal bleeding that is not associated with the menstrual cycle.
Endometrial cancer mostly occurs in post-menopausal women. Symptoms like pain with urination, during sexual intercourse, or pelvic pain or seen in women with endometrial cancer. Endometrial cancer sometimes is also referred to as uterine cancer.
Endometrial cancer is diagnosed by endometrial biopsy or by taking samples during dilation and curettage procedure. Abdominal hysterectomy is a leading treatment option for This endometrial thickness treatment. This involves the removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries on both sides.
Vaginal bleeding, uterine bleeding, and abnormal menstrual cycles are common symptoms. The diagnosis is done through transvaginal ultrasound to examine the endometrial stripe thickness range in women with postmenopausal bleeding.
Endometrial cancers or classified into the following types
Carcinoma - type I and type II
Type I endometrial carcinoma occurs before the menopausal period and at the time of menopausal in women.
Type II endometrial carcinoma occurs in older, postmenopausal women and is not associated with endometrial hyperplasia.
Endometrioid adenocarcinoma
In endometrioid adenocarcinoma, the cancer cells grow in patterns reminiscent of normal endometrium. Many new glands are formed from columnar epithelium with abnormal nuclei.
Serous carcinoma
Serous carcinoma is a Type II endometrial tumor that is common in postmenopausal women with atrophied endometrium. It appears with many atypical nuclei, papillary structures, and rounded cells instead of columnar cells.
Mucinous carcinoma
It is a rare form of endometrial cancer and occurs in less than 1-2% of all endometrial cancers. Well-differentiated columnar cells organized into glands with characteristic mucin in the cytoplasm can be seen.
Mixed or undifferentiated carcinoma
Mixed carcinomas have both- type I and type II cells. These include malignant mixed Mullerian tumors derived from the endometrial epithelium.Undifferentiated endometrial carcinoma has a prognosis more than grade III tumors. These tumors show sheets of identical epithelial cells with no identifiable pattern.
Other carcinomas
Non-metastatic squamous cell carcinoma and transitional cell carcinoma for the rarest carcinomas that occurred. The common genetic causes are uncategorized and there are no guidelines on how to treat this type of cancer.
Sarcoma
Sarcomas or uncommon endometrial cancers begin in the non-glandular connected issue of the endometrium. These are generally nonaggressive and if they reoccur can take decades to get cured.
Treatment of endometrial stripe thickness in endometrial cancer
Thickened endometrium treatment in the case of endometrial cancer include surgery to remove the uterus, fallopian tubes. Radiation therapy with high energy is another option for thickened endometrium treatment in endometrial cancer.
Other options to thickened endometrium treatment include chemotherapy with powerful drugs and hormone therapy to block the hormones that cause the proliferation of the cells.Targeted therapy is another option to treat endometrial stripe thickness in endometrial cancer which involves drugs that attack specific weaknesses of the cancer cell. Immunotherapy will help to boost the immunity to fight against endometrial cancer.
4. Endometrial receptivity
Endometrial receptivity is a complex process that helps the embryo in providing the opportunity to attach, invade and develop into a new individual for the continuation of the species.
The window of implantation is 3 to 6 days within the secretory phase. Endometrial receptivity plays a major role to preclude normal implantation, fertility, or pregnancy outcome. The ovarian response is also important for clinical pregnancies besides endometrium.
Importance of endometrial thickness and endometrial receptivity on pregnancy outcome
A retrospective cohort study was conducted to understand the relation between endometrial thickness or thin uterine lining symptoms and clinical pregnancies that are caused due to unstimulated menstrual cycles.
Even though it is proven that endometrium is important for the development and maintenance of pregnancy outcomes, it is unclear which endometrial factors are relevant. During transvaginal ultrasound evaluation, endometrial thickness, echo pattern, and endometrial perfusion are evaluated.
The significance of endometrial thickness has been investigated in in-vitro fertilization treatments [IVF- clinical pregnancies] and reproductive technology with ovarian response.
The association of pregnancy outcome with endometrial thickness in unsimulated menstrual cycles with fresh embryo transfers was described in this retrospective cohort study. The study evaluation was adjusted to factors that influence the pregnancy outcome and the endometrial thickness.
This retrospective cohort study of endometrial thickness has shown the following data
In all the studies, the association of endometrial thickness with pregnancy outcome rate was performed only with high dose IVF (clinical pregnancies) stimulations, reproductive technology like cryopreserved embryos, or low dose Intra Uterine Insemination (IUI) stimulations.
The retrospective cohort study has confirmed the reduced pregnancy outcome with endometrial thickness of ≤ 7 mm. The reason for the reduced pregnancy outcome in patients undergoing GnRH stimulated IVF therapy compared to endometrial thickness > 7 mm is unclear.
In contrast, a lower pregnancy outcome is observed in women with thick endometrium lining. But an increased pregnancy outcome is not confirmed with particularly thick endometrium lining of > 11 mm, > 13 mm, > 14 mm with GnRH stimulated IVF therapies.
Also found that there is no significant correlation between endometrial thickness and pregnancy outcome in hormone-stimulated reproductive technology (IUI) treatments.
Lower pregnancy outcomes with thin uterine lining symptoms could be inherited if it significantly affected fertility. Other factors can influence lower pregnancy outcomes due to thin uterine lining such as exposure of the uterus to radiation, multiple curettages.
In the end, this prospective cohort study has concluded along with thick endometrium lining that thin endometrium is also associated with lower pregnancy outcomes in unsimulated menstrual cycles.
What is endometriosis?
Endometriosis is a disease of the female reproductive system where the presence of normal endometrial mucosa is seen in locations other than the uterine cavity. It usually occurs on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, tissue around the uterus and ovaries, and in rare cases, it may occur in other parts of the body too.
Symptoms include pelvic pain, heavy periods, pain with bowel movements, and infertility. The cause of endometriosis is not known but can affect pregnancy outcomes or clinical pregnancies.
A biopsy is the surest method of diagnosis.
Treatment for endometriosis
As there is no cure for endometriosis, treatment of pain and treatment of endometriosis-associated infertility are the only management procedures. Pharmacotherapy is initiated for pain management based on the symptoms and examination of endometrial stripe thickness by transvaginal ultrasound.
To restore or preserve fertility, endometriosis is treated exceptionally with reproductive technology like surgery, fertility medication, or IVF (clinical pregnancies). Usually, surgery is done through the laparoscopic method. During the fertility treatment, ultra-long pre-treatment with the GnRH agonist has a higher chance of resulting in pregnancy with endometriosis when compared to short pre-treatment.
Take-Home Points
Normal endometrial thickness in healthy women will change according to the age and phases of life.
Endometrial thickness normal size in mm in post-menopausal women is < 5 mm.
Endometrial thickness normal size in mm during menstrual cycles is around 14 mm and if someone is taking tamoxifen, endometrium normal size in mm is less than 5mm.
Abnormal vaginal bleeding can be due to endometrial hyperplasia, endometrial cancer, pregnancy outcome, abortion or vaginal injury.
Endometrial cancer causes thick endometrial lining. Endometrial hyperplasia when left untreated can lead to endometrial cancer.
Consult a gynecologist if you observe any abnormal vaginal bleeding or uterine bleeding.
Medications, hormonal therapy, surgery can be done to correct the endometrial thickness in women.
Endometrial thickness exhibits a relationship with pregnancy outcomes in fresh embryo transfer cycles.
Thin uterine lining and thick endometrial lining are associated with the ovarian response but not important predictors of clinical pregnancies.
References
FAQ on Endometrial Thickness - What is Normal Size of Endometrium in mm?
A endometrial thickness of 14 mm is considered normal during the menstrual cycle. However, it's important to note that endometrial thickness can vary depending on factors such as age, phase of the menstrual cycle, and use of hormonal medications. Additionally, abnormal vaginal bleeding or other symptoms may warrant further evaluation by a healthcare provider to determine if there are any underlying issues that need to be addressed.
Endometrial thickness normal range in postmenopausal women are less than 5 mm. However, an endometrial thickness measurement of 7 mm after menopause may not necessarily indicate a significant health concern on its own. The thickness of the endometrium can be affected by various factors such as hormonal changes, medications, or underlying medical conditions. However, an endometrial thickness measurement of 7 mm or greater may warrant further evaluation to rule out any potential underlying health issues, particularly if there are other concerning symptoms or factors present. It is important to speak with a healthcare provider who can provide a proper evaluation and diagnosis based on your individual medical history and symptoms.
The optimal endometrial thickness for conception can vary depending on a variety of factors, including age, menstrual cycle phase, and individual health status. However, in general, an endometrial thickness of 8-14 mm is considered optimal for conception, with some studies suggesting that a thickness of at least 7 mm may be sufficient for successful implantation and pregnancy. However, it's important to keep in mind that endometrial thickness alone is not the only factor that affects fertility and successful conception. Other factors such as hormonal balance, ovarian function, and sperm quality also play important roles. If you are experiencing difficulty conceiving, it's important to seek the advice of a healthcare provider who can evaluate your individual situation and recommend appropriate treatments or interventions to help increase your chances of successful conception.
The treatment for abnormal endometrial thickness depends on the underlying cause and individual health status. Hormonal therapy, such as progesterone or estrogen-progesterone combinations, may be prescribed to regulate the thickness of the endometrial lining. Medications to treat underlying conditions, like endometrial hyperplasia or endometriosis, may also be necessary. In some cases, surgical intervention may be required to remove abnormal tissue or growths. Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, reducing stress, and exercising regularly, can promote overall reproductive health and improve endometrial thickness. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential in determining the most appropriate treatment options based on individual health history and underlying causes of endometrial thickness.
Thickened endometrium treatment depends on the cause and individual health status. Hormone therapy or adjusting medication can reduce thickness caused by hormonal imbalances or medication side effects. More serious conditions like endometrial hyperplasia or cancer may require surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy to control abnormal cell growth. Successful treatment depends on factors such as severity, overall health, and timely intervention. Many cases can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment, leading to good health outcomes.
The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus that thickens and sheds during the menstrual cycle. Thickening beyond normal is known as endometrial hyperplasia, caused by various factors like hormonal imbalances, obesity, PCOS, and certain medications. Symptoms include abnormal bleeding, prolonged periods, and pelvic pain. Diagnosis via tests such as ultrasound, biopsy, and hysteroscopy. Treatment depends on severity and cause, ranging from hormonal therapy for mild cases to surgery, and even hysterectomy in extreme cases.
The thickening of the endometrium is a natural process during the menstrual cycle, but endometrial hyperplasia can be prevented by maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, eating a balanced diet, limiting alcohol intake, managing underlying conditions, and having regular gynecological check-ups to detect any abnormalities early.
Normal endometrial thickness varies based on menstrual cycle phase and age. In premenopausal women, normal range is 2-4mm during menstrual phase to 7-16mm during secretory phase. Postmenopausal women have normal range less than 5mm. Abnormally thick endometrium may be a concern in cases of abnormal vaginal bleeding, postmenopausal bleeding, fertility issues, or HRT. If identified, further evaluation by healthcare provider is necessary for appropriate treatment plan.
A thin uterine lining can make it difficult for a fertilized egg to implant, but pregnancy is still possible. Underlying medical conditions and hormonal imbalances may cause a thin uterine lining. Medications like estrogen can promote growth, and IVF may be recommended. Despite the challenge, there are still ways to increase chances of conception by discussing with a healthcare provider.
An endometrial thickness greater than 5mm in postmenopausal women and greater than 14mm in women during their menstrual cycle is considered abnormal.
In premenopausal women, an endometrial thickness of 10mm may be considered normal during the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle. However, endometrial thickness can vary based on the menstrual cycle phase and individual factors, so it's important to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider. In postmenopausal women, an endometrial thickness greater than 5mm may be considered abnormal and require further evaluation.
Yes, losing weight can be beneficial for women with endometrial hyperplasia. Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition in which the lining of the uterus (the endometrium) becomes thicker than normal, which can lead to abnormal bleeding or an increased risk of developing endometrial cancer. Obesity is a known risk factor for endometrial hyperplasia, and losing weight can help decrease the amount of estrogen in the body, which can reduce the risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia. However, it's important to note that weight loss alone may not always be sufficient to treat endometrial hyperplasia, and it's important to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for individual cases. In some cases, medication or surgery may also be necessary to manage the condition.
While there is no specific food that has been proven to increase endometrial thickness, certain foods can support reproductive health and potentially contribute to healthy endometrial thickness. These foods include dark leafy greens, broccoli, beans, nuts, and seeds, which are rich in iron. Additionally, salmon, sardines, trout, chia seeds, and flax seeds are good sources of essential fatty acids that may also support reproductive health.
Endometrial hyperplasia occurs due to the overgrowth of the endometrial lining in the uterus, which can be caused by hormonal imbalances, obesity, PCOS, Tamoxifen use, and genetic mutations. It is not always known what causes endometrial hyperplasia, but it is essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine whether treatment or monitoring is necessary. Endometrial thickening is not always a cause for concern, and in many cases, it may resolve on its own.
Yes, endometrial thickness can change with age. In premenopausal women, endometrial thickness varies throughout the menstrual cycle, and it typically reaches its thickest point just before menstruation. In postmenopausal women, the endometrial lining tends to thin out due to the lower levels of estrogen, which is a hormone that stimulates endometrial growth.
An endometrial thickness of 7.5 mm may be considered normal during certain stages of the menstrual cycle, but it may be on the lower side for preparing for pregnancy or fertility treatment.
The normal range of endometrial thickness can vary depending on the stage of the menstrual cycle and the woman's age, but generally, a thickness of 8-11 mm during the ovulatory phase is considered normal for women of reproductive age.
The thickness of the endometrium is an important factor in fertility and pregnancy, but it is not necessarily an indication of a serious medical condition on its own.
The normal size of the endometrium to get pregnant varies depending on the stage of the menstrual cycle, but generally, a thickness of 8-11 mm during the ovulatory phase is considered normal for women of reproductive age.
An endometrial thickness of 20 mm may be considered normal in some cases, such as during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, but it can also indicate the presence of abnormal growths or other medical conditions.
It may be more difficult to get pregnant with an endometrial thickness of 7.5 mm, but it is still possible, particularly with fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
A thickness of 9.2 mm can be considered normal during certain stages of the menstrual cycle, but it is on the lower side for preparing for pregnancy or fertility treatment.
A thickness of 8.2 mm can be considered normal during certain stages of the menstrual cycle, but it may be on the lower side for preparing for pregnancy or fertility treatment.
A good size endometrium depends on the stage of the menstrual cycle, but generally, a thickness of 8-14 mm during the ovulatory phase is considered good for women of reproductive age.
Endometrial thickness can be considered abnormal if it is either too thin or too thick for the stage of the menstrual cycle, or if it is associated with certain medical conditions or abnormal growths.
For women undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF), a thickness of at least 8 mm is generally desired for optimal chances of pregnancy.
While there is no specific food that can increase endometrial thickness, a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins may be beneficial for overall reproductive health.
Yes, it is possible to get pregnant with an endometrial thickness of 11 mm.
The endometrial thickness varies from person to person. A thickness of 15mm in women can be considered normal if she is not experiencing menopause.
The endometrial thickness of 15mm in a lady of the fertile age I.e before menopause is considered normal or if you are on hormonal medications. But if you have attained menopause, 15mm endometrial thickness is not normal and you should consult a gynecologist soon.
Normal endometrial thickness for a lady in her reproductive years is between 8mm to 15mm, unless she is pregnant, because then the endometrial thickness increases.
Endometrial thickness of 5mm is normal if you are postmenopausal, but for someone in reproductive age, it is not healthy and one must see a doctor soon.
Depending on your age, 7mm endometrial thickness may be normal or unhealthy. You must consult your gynecologist for the same because healthy endometrial thickness depends on various factors.
Endometrial thickness less than normal or more than normal for the given age group is considered bad.
The endometrial thickness varies from person to person and age to age. For someone in reproductive age, healthy endometrial thickness is between 8mm to 15mm. Though even during this age group, it varies according to your menstrual cycle.
The normal endometrium thickness is 8mm to 15mm for a Lady in her reproductive years.
Comments ( 0 )
No Comments
Leave a Comment
Related Posts
Diarrhea in Pregnancy - Treatment and Home Remedies for Diarrhea during Pregnancy
Get relief from diarrhea during pregnancy. Learn about safe treatment and home remedies to ensure a healthy pregnancy journey.
Neeraja H
Relationship Problems and Pregnancy: How to solve Relationship Stress during Pregnancy
Pregnancy is all about happy memories but mood swings in pregnancy can cause relationship problems. Pregnancy mood swings can be kept in check with effective tips.
Manasa Krishna Perumalla
Ovulation Pain (Mittelschmerz): Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
Ovulation pain also known as mittelschmerz is a dull ache or cramp in the lower abdomen around ovulation time.
Keerthana A P
PCOD VS PCOS: Difference, Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
PCOS vs PCOD - What is the difference between PCOD and PCOS? Learn about the signs, symptoms, causes, and treatment of the two.
Manasa Krishna Perumalla
15 Home Remedies for Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a painful condition that affects millions of women. Find relief with these 15 natural home remedies for Endometriosis
Juveriya Anwar Momin
Endometriosis: Diet and Exercises for endometriosis patients
Discover how diet and exercise can help manage endometriosis symptoms. Learn about the best foods and workouts to improve overall well-being. Expert advice and practical tips.
Dr. Mrinalinee Roy
Health & Wellness Tips
Subscribe to our blog